Ce thème de recherche du SPEC porte sur l’élaboration et l’étude de :
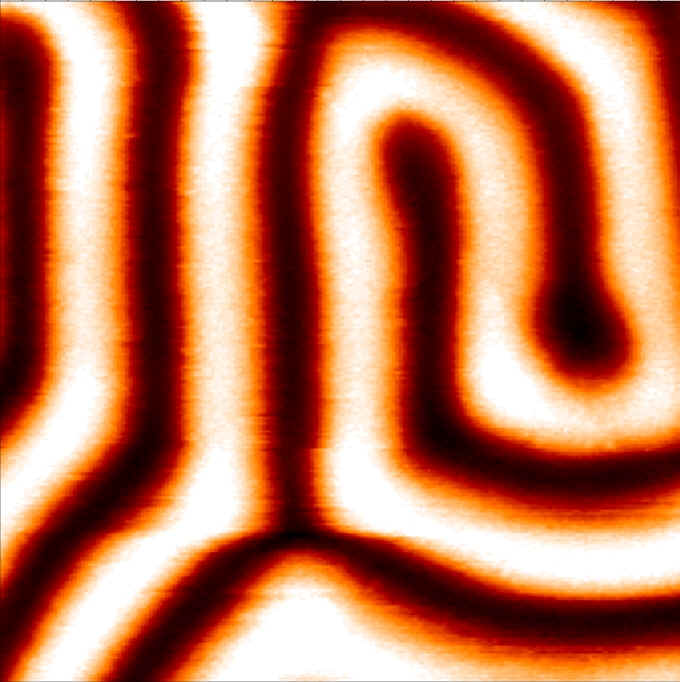
- matériaux oxydes magnétiques ou multiferroïques* (ferroélectricité associée au magnétisme)
- la dynamique de l’aimantation dans les nanostructures hybrides et son couplage aux courants de spin (spintronique)
- le développement de capteurs de champ magnétique ultra-sensible
- et la modélisation associée.
Ces études utilisent de nombreuses techniques maitrisées au SPEC :
- croissance de film minces (oxydes en particulier),
- mesures de transport et magnétiques,
- diffusion de neutrons (polarisés),…

La caractérisation des capteurs magnétiques est réalisée dans une installation « ultra-bas bruit magnétique » spécialement dédiée, indispensable au développement de multiples applications : contrôle non destructif, sécurité, capteurs de vitesse, capteurs de courant… .
Le groupe « Nanomagnétisme et Oxydes (LNO) » du SPEC a son activité entièrement centrée sur cette thématique.
Le groupe « Modélisation et théorie (GMT) » explore par simulation atomistique l’ensemble de ces systèmes et leurs propriétés.
*Les matériaux multiferroïques sont des matériaux multifonctionnels, car ils possèdent simultanément plusieurs propriétés « ferroïques » : ferromagnétisme, ferroélectricité et/ou ferroélasticité. Leurs élaboration en couches minces permet de réaliser des objets fonctionnels, où plusieurs propriétés couplées peuvent être exploitées.