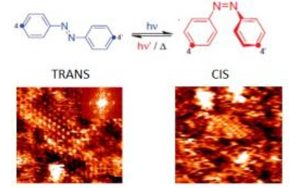
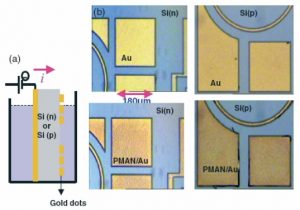
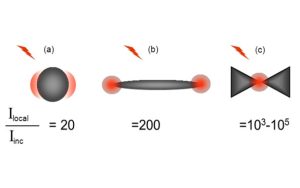
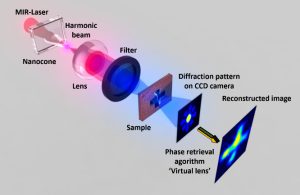
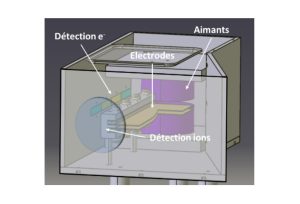
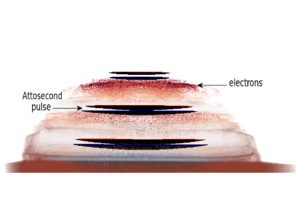
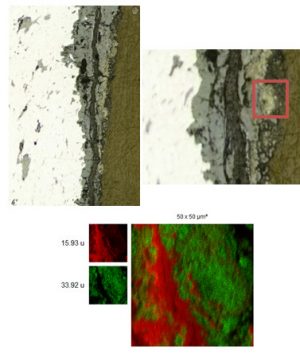
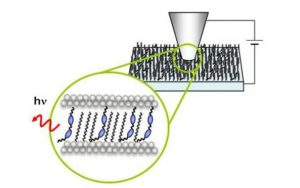
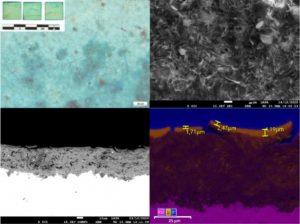
Nos projets de recherches sont financées par diverses sources : l’Europe, l’ANR, la région, des collaborations industrielles…
|
Projets de recherche – En cours
-
-

-
-
-

-

-

-
-

-

-
-

-
-
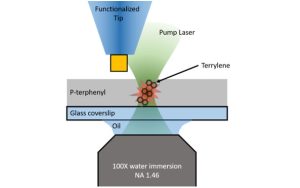
-
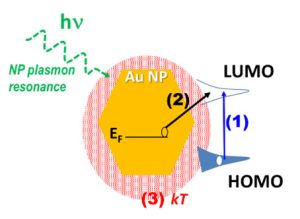
-
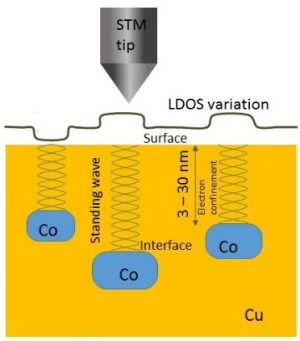
-

-

-

-

-

-
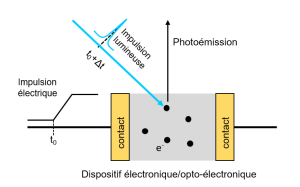
-
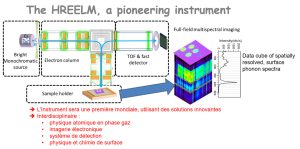
-
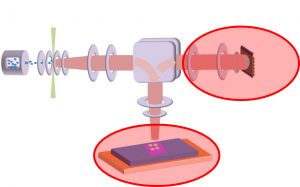
-
-
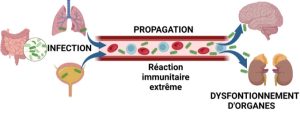
-
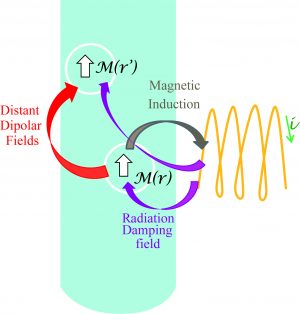
-

-
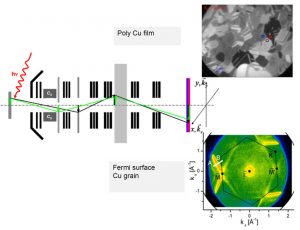
-

-

-

-
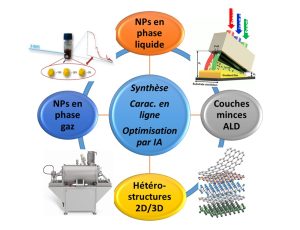
-

-
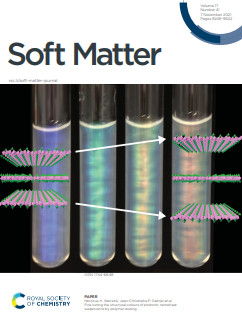
-

-
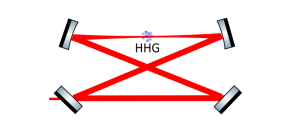
-
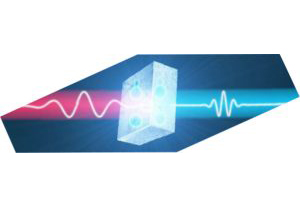
-

-
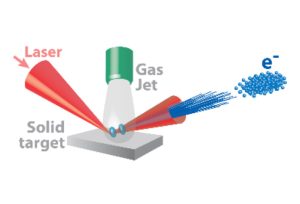
-
-

-

-

-

Projet ANR NANOLITE
2019 -
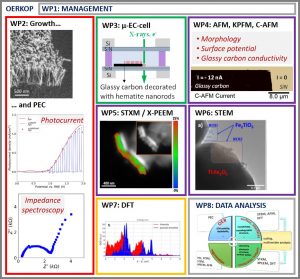
Projet ANR OERKOP
2023 -

-

-

-

-

-
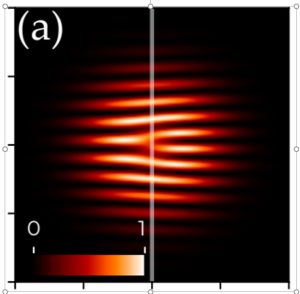
-
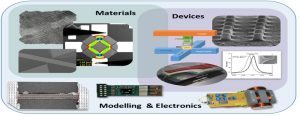
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-
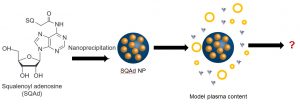
-

-
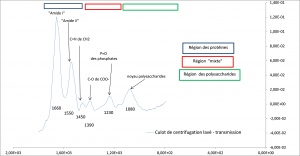
-

-
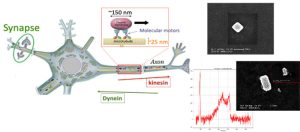
-
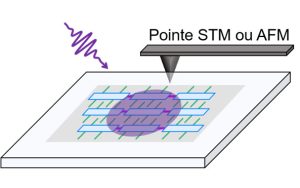
-

-

-

-

-

-

-

-