Benjamin Pigeau, Grégoire de Loubens, and Olivier Klein: Groupe Nanomagnétisme
In a vortex-state magnetic nanodisk, the static magnetization is curling in the plane, except in the disk center where it is pointing out-of-plane, either up (polarity p=+1) or down (p=-1). The lowest energy excitation mode of this ground state is the so-called gyrotropic mode [1], corresponding to a gyration of the vortex core around its equilibrium position at the center of the disk. In zero magnetic field, the resonant frequency of this mode is insensitive to the magnetization direction in the core, but the sense of the core rotation is determined by a right-hand rule to its polarity. Recent experiments performed at zero field demonstrated reversal of vortex core polarity through large amplitude excitation of the gyrotropic mode [2]. This dynamical reversal mechanism is of fundamental interest but also has potential application in information technology, with the vortex core polarity coding the binary information.
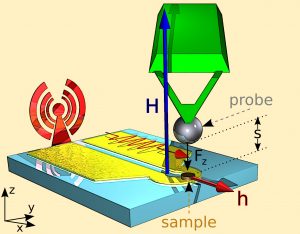
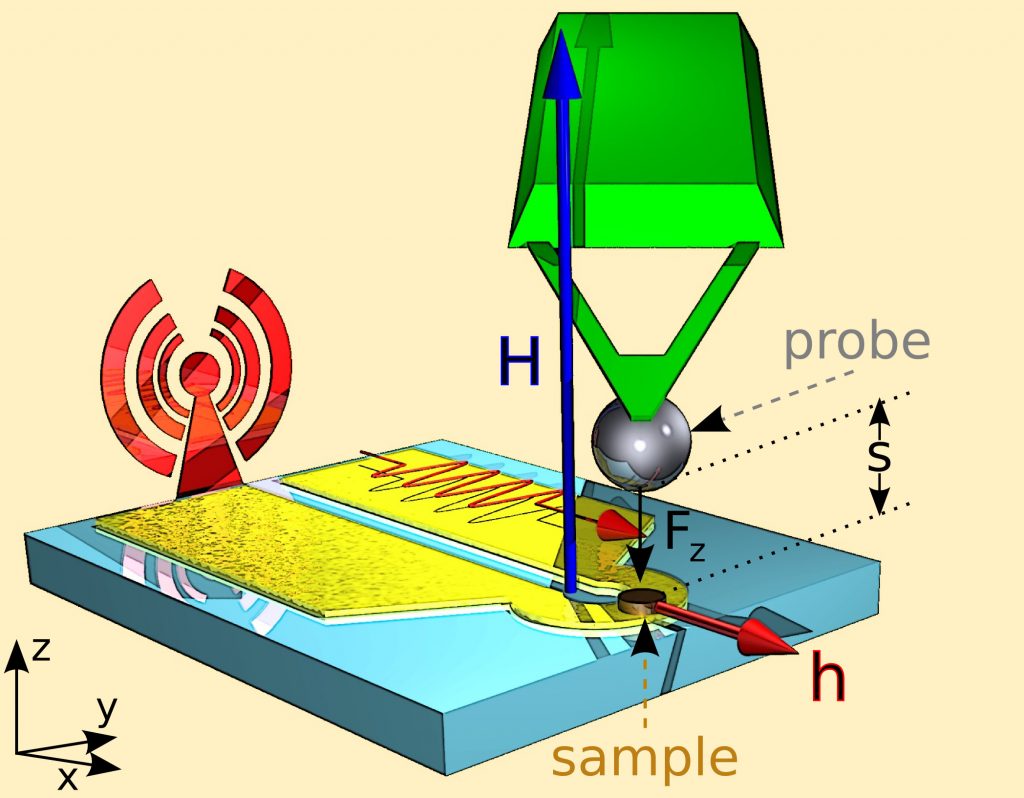
In order to investigate magnetization dynamics in individual vortex-state nanodisks, we have used the exquisitely sensitive technique of magnetic resonance force microscopy (MRFM), developed in the Nanomagnetism Group of SPEC [3] (see Fig. 1). The studied nanodisks with thickness 44 nm and diameter 1 µm are made of NiMnSb alloy, an ultra-low damping epitaxial material grown in Laurens Molenkamp's group (Würzburg Universität).
 |
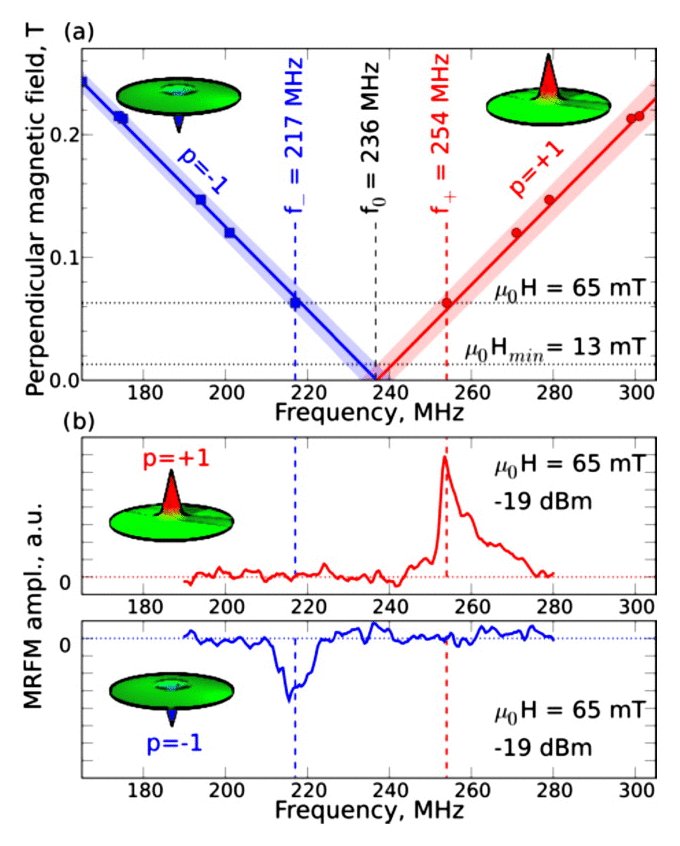 |
We have first demonstrated that the frequency degeneracy corresponding to the gyrotropic modes with opposite polarities in zero field can be lifted by applying a magnetic field perpendicular to the disk plane [4] (see Fig. 2). This Zeeman-like splitting can be used for a simple reading of the polarity state in an individual nanodisk. In order to discriminate the resonant frequencies f– and f+ associated respectively to the core polarities p=-1 and p=+1, it is necessary to choose the static magnetic field in such a way that the field-induced gyrotropic frequency splitting exceeds the linewidth of the gyrotropic mode. In our experiment, a bias field as small as µ0H=13 mT is sufficient to fulfill this condition. Obviously, the microwave magnetic field employed to read the polarity state must be weak enough, so that the core polarity is not reversed during the reading sequence.
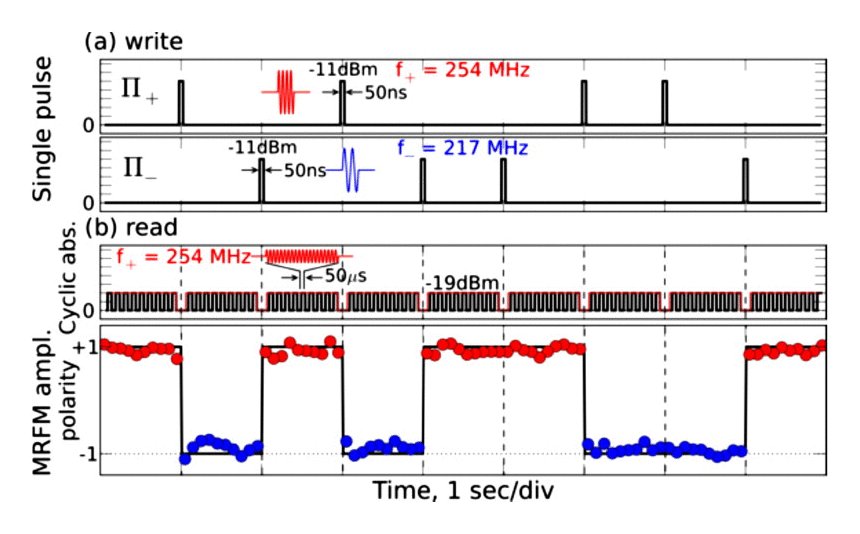
We can also take advantage of this frequency discrimination in order to reverse deterministically the vortex core polarity, as shown in [5]. Starting with the vortex core polarity in, say, the p=+1 state, a single microwave field pulse whose carrier frequency is tuned at f+ and with sufficient amplitude (that we shall call a Π+ inversion pulse) will resonantly excite the gyrotropic motion of the core until it reaches the critical threshold for reversal. Once it has been reversed, the final state p=-1 is out of resonance with the writing pulse, so that it cannot be switched back to p=+1. Similarly, it is possible to write the state p=+1 starting from the p=-1 state using the appropriate Π– pulse (see Fig. 3). This writing process has been shown to be very robust, as no mistake could be recorded out of several hundred attempts with our experimental parameters.
In sum, our frequency-controlled magnetic vortex memory prototype has two main advantages. Owing to the frequency discrimination allowed by a small perpendicular bias field, there is no need to control the circular polarization of the microwave field and to precisely time the writing pulse as it has to be in zero field. Also, deterministic and local addressing in a large array of memory cells is easily obtained by using the stray-field of the MRFM probe, that can be scanned laterally. Finally, a series of improvements can be imagined in order to make our memory prototype more practical. In particular, it would be useful to replace the MRFM detection by electrical detectors, and to use a local combination of the static and microwave fields at the intersection of a word and a bit lines to address the binary information in individual cells.
References:
[1] Magnetic vortex state stability, reversal and dynamics in restricted geometries
K. Y. Guslienko, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 8, 2745 (2008).
[2] B. V. Waeyenberge, A. Puzic, H. Stoll, K. W. Chou, T. Tyliszczak, R. Hertel, M. F¨ahnle, H. Brückl, K. Rott, G. Reiss, I. Neudecker, D. Weiss, C. H. Back, and G. Schütz, Nature (London) 444, 461 (2006).
[3] Ferromagnetic resonance force spectroscopy of individual submicron-size samples
O. Klein, G. de Loubens, V.V. Naletov, F. Boust, T. Guillet, H. Hurdequint, A. Leksikov, A.N. Slavin, V.S. Tiberkevich, N. Vukadinovic, Phys. Rev. B 78, 144410 (2008).
[4] G. de Loubens, A. Riegler, B. Pigeau, F. Lochner, F. Boust, K.Y. Guslienko, H. Hurdequint, L. W. Molenkamp, G. Schmidt, A. N. Slavin, V.S. Tiberkevich, N. Vukadinovic, O. Klein, Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 177602 (2009).
[5] B. Pigeau, G. de Loubens, O. Klein, A. Riegler, F. Lochner, G. Schmidt, L.W. Molenkamp, V.S. Tiberkevich, A.N. Slavin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 132506 (2010).