Contact: Agustin Palacios-Laloy and Denis Vion
(
The violation of J. Bell's inequalities with two spatially separated objects is often considered as the most prominent demonstration of the quantum nature of our world: the objects can be so intimately entangled that speaking of the state of each object loses its meaning even when they are far apart. The famous experiment by A. Aspect's team, in which the two objects were polarized light particles (photons), was a perfect demonstration of such a non local realism.
Subsequently, A. Leggett (2003 Nobel Prize winner in physics) has proposed a similar inequality that holds for a single object measured at successive times, hence the name “Bell's inequality in time”. As reported in Nature Physics, this inequality has just been tested experimentally by the members of Quantronics, a research group at the CEA (IRAMIS-SPEC). The results demonstrate the violation of Bell's inequality in time as predicted by quantum mechanics.
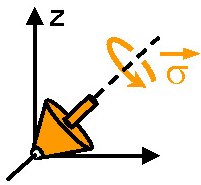
In this experiment the measured object is a superconducting electrical circuit (in orange in figure b) that behaves as the simplest quantum mechanical system; i.e., a spin ½ (a quantum analogue of a spinner rotating around its own axis σ, shown in orange in figure a). This spin is made to rotate around another axis, X, by an externally applied electromagnetic field Vd (in magenta), while its projection onto the Z-axis, σz, is measured continuously by an oscillator driven by another field Vm (in green). The time correlation function C(t)=<σz(t0) σz(t0+t)> of the measured signal σz(t) violate the inequality fL(t)= 2C(t)- C(2t) ≤ 1 established by Leggett for a classical object. The experimentally determined fL(t) (red points and error bars in figure c) follows precisely the quantum mechanical predictions (blue curve) and violate the inequality at short times (indicated by the green arrow).
This observation shows the truly quantum mechanical character of the superconducting electrical circuit; that is, it has no defined state unless it is measured and it can't be measured without perturbing its dynamics in a profound way.
Références :
|
Experimental violation of a Bell's inequality in time with weak measurement A. Palacios-Laloy1, F. Mallet1, F. Nguyen1, P. Bertet1, D. Vion1, D. Esteve1 and A. N. Korotkov2, Nature Physics, 6 (2010) 442. |
– See also “New and Views” in Nature :
Quantum mechanics: No moon there, Johan E. Mooij, Nature 6 (2010) 401.
“An experiment reveals that micrometre-sized superconducting circuits follow the laws of quantum mechanics, and thus defy common experience of how macroscopic objects should behave”.
|
– CEA press release. |
 |
– WEB site of the quantronic group in IRAMIS-SPEC



