Dispositif et procédé de caractérisation d'un faisceau de lumière.
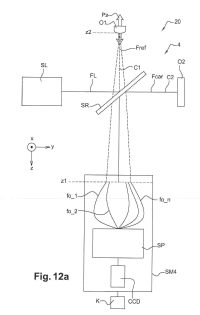
L'invention concerne un procédé de caractérisation d'un faisceau de lumière comprenant les étapes suivantes : – séparation au moyen d'une optique séparatrice du faisceau de lumière en un premier sous-faisceau et un deuxième sous-faisceau; – propagation du premier sous-faisceau sur une première optique et du deuxième sous-faisceau sur une deuxième optique, lesdites première et deuxième optiques étant respectivement agencées de sorte que le premier sous-faisceau en sortie de la première optique, dit « faisceau de référence », et le deuxième sous-faisceau en sortie de la deuxième optique, dit « faisceau à caractériser », présentent entre eux un délai temporel τ balayant un intervalle de temps T1 avec un pas P1; – recombinaison au moyen d'une optique recombinatrice du faisceau de référence et du faisceau à caractériser de telle manière qu'ils interfèrent spatialement et forment un motif d'interférence bidimensionnel; – mesure au moyen d'un système de mesure dudit motif d'interférence bidimensionnel en fonction du délai temporel τ balayant l'intervalle de temps T1 avec le pas P1, pour l'obtention d'un interférogramme temporel; – calcul de la transformée de Fourier dans le domaine fréquentiel d'au moins un point spatial de l'interférogramme temporel, ladite transformée de Fourier dans le domaine fréquentiel présentant un pic fréquentiel central et des premier et deuxième pics fréquentiels latéraux; – calcul de l'amplitude spectrale AR(ω) et de la phase spatio-spectrale φR(x,y,ω) pour l'un desdits premier et deuxième pics fréquentiels latéraux de ladite transformée de Fourier dans le domaine fréquentiel..
Device and method for characterization of a light beam (WIPO link)
The invention concerns a method for characterization of a light beam, comprising the following steps: – separation of the light beam by means of a separator optic into a first sub-beam and a second sub-beam; – propagation of the first sub-beam over a first optic and of the second sub-beam over a second optic, said first and second optics being respectively arranged so that the first sub-beam on leaving the first optic, referred to as the “reference beam”, and the second sub-beam, on leaving the second optic, referred to as the “characterized beam”, are separated by a time delay τ sweeping a time interval T1 with step P1; – recombination of the reference beam and the characterized beam by means of a recombiner optic in such a way that the beams spatially interfere and form a two-dimensional interference pattern; – measurement of said two-dimensional interference pattern by means of a measurement system, as a function of the time delay τ sweeping the time interval T1 with step P1, in order to obtain a temporal interferogram; – calculation of the Fourier transform in the frequency domain of at least one spatial point of the temporal interferogram, said Fourier transform in the frequency domain having a frequency central peak and first and second frequency side peaks; – calculation of the spectral amplitude AR(ω) and of the space-spectrum phase φR(x,y,ω) for one of said first and second frequency side peaks of said Fourier transform in the frequency domain.
Contact : F. Quere (IRAMIS/LIDYL)