The study of the development of functional nanocomposite thin layers is being developed as part of the ANR HYMALAYAN project (2015-2019). This project proposes the production by an original process, in a single step and in a confined manner, of nanocomposite layers controlled in situ.
The nanocomposites are in the form of nanoparticles (NPs) of 4 to 100 nm distributed homogeneously in a matrix (see Figure 1), without limitation of relative chemical compositions between the nanoparticles and the matrix. The process combines vacuum nanoparticle jets (NVJ) and vapor deposition (PVD). It takes advantage of the flexibility of JNVs produced by aerodynamic lenses1, which make it possible to adapt to any NP synthesis method, and that of PVD allowing the growth of any type of matrix.
The hybridization of these two techniques is made possible by transporting the nanoparticles aerodynamically to the substrate, either immediately after their synthesis or from a colloidal suspension. The simultaneous deposition of the particles and the matrix is carried out on the same face of the same substrate. The process is innovative in that it allows an a priori unlimited choice in the respective chemical compositions of the nanoparticles and the matrix. The characterization of the layers is carried out online during deposition by in situ ellipsometry.
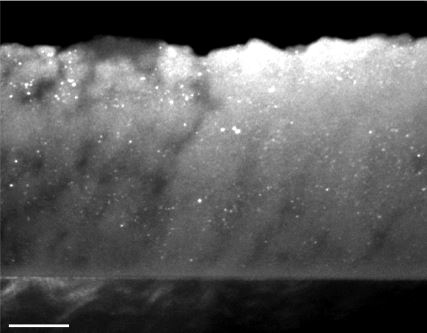
The source of nanoparticles can be provided by a process for synthesizing NP in the gas phase (laser pyrolysis), which makes it a completely “safe-by design” process, since the syntheses of the NP and the nanostructured material are carried out in one. single step and in the same confined device. The project has three main axes:
- Optimization of the process for large surfaces,
- Characterization of deposits (in situ and ex situ)
- The development of composites for industrial applications.
Our industrial development effort aims to explore and demonstrate all the flexibility and performance of this innovative process on substrates with a surface area of around 10 x 10 cm2. A first action, led by the company DECAYEUX-STI, concerns the production of coatings of gold nanoparticles or other precious metals in a SiO2 matrix on manufactured objects in the luxury sector. The objective is to obtain adherent and dense layers presenting a specific aesthetic appearance rendered by the optical properties of the nanoparticles. The second part, led by CEA/IRAMIS, aims to improve the efficiency of silicon photovoltaic cells by developing a material composed of silicon nanocrystals doped in a dielectric matrix.
[1] In-situ characterization of nanoparticle beams focused with an aerodynamic lens by laser-induced breakdown detection
F.-A. Barreda, C. Nicolas, J.-B. Sirven, F.-X. Ouf, J.-L. Lacour, E. Robert, S. Benkoula, J. Yon, C. Miron & O. Sublemontier, Sci. Report 5 (2015) 15696 .
Contact : Olivier Sublemontier.


