French contribution to ESS instrumentation
Introducing the European Spallation Source
The ESS (European Spallation Source) is the next-generation European spallation source currently under construction in Lund (Sweden). Using a long-duration neutron pulse (2.86 ms compared with the usual ~100 µs) clocked at 14 Hz, it will produce an integrated neutron flux equivalent to that of the ILL (link to presentation poster).
Artist’s view of the ESS website (see the video)
The pulsed nature of the source makes it possible to use the temporal structure of the neutron beam to determine the energy of the incident neutrons, eliminating the need for a monochromator for the vast majority of instruments. The usable flux at the sample position is thus naturally multiplied by the full use of the poly-chromatic beam.

Comparison of ESS neutron pulses and spallation sources in operation.
Two moderators, cold and thermal, will be installed, giving users access to a neutron spectrum covering the range ~0.5 to ~20 Å. The instruments are due to be available to outside users in 2023, with on-site installation of the components essential for starting up the source underway, and the instrumentation in the detailed design phase.
In-kind French contribution
In preparation for the launch of ESS, 15 instruments have been selected for their ability to meet the needs of the European scientific community, as well as for their unique features. These instruments are financed and built through in-kind contributions from ESS partners. These in-kind contributions cover the design, component reception, installation, integration and cold commissioning phases. France contributes 8% of the total ESS construction budget (1843 M€), of which 35 M€ is dedicated to instrumentation.

3D view of the instrument suite under development.
Within this framework, LLB is involved in the construction of 6 instruments (3 diffractometers, 2 spectrometers and a SANS – Small Angle neutron Scattering) and part of the shared sample environment for the instruments.
- Type : diffractomètre de neutrons polarisé dédié à l’étude des propriétés magnétiques sur mono-cristaux.
- Contributeurs : LLB (~60%), JCNS (~24%) et PSI (~16%)
- Personnels LLB : S. Klimko, T. Robillard, A. Goukasov, X. Fabrèges
- Capacités : résolution de structures magnétiques, densité de spin, susceptibilité/anisotropie/aimantation locale, polarisation XYZ et analyse de polarisation, haut flux et petits échantillons.
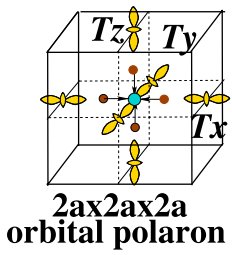
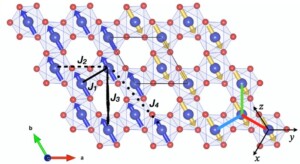
- Thématiques couvertes : matériaux multi-fonctionnels, supraconductivité, couplage spin-orbite, magnétisme fondamental, magnétisme moléculaire, chiralité, skyrmions, couches minces et interface, magnétisme quantique.
- Type : spectromètre temps de vol froid à géométrie directe.
- Contributeurs : LLB (50%) et TUM (50%)
- Personnels LLB : F. Y. Moreira, G. Fabrèges, S. Longeville
- Capacités : multi-échelles (1 – 1000 Å et 10-14 – 10-10 s), petits échantillons, expériences pompe/sonde, cinétique in-operando, hautes pressions, mesures sous champs électrique.
- Thématiques couvertes : matière molle, stockage de l’hydrogène/CO2, catalyse, magnétisme, batteries, life science, …
- Type : spectromètre multifonctions de Diffusion des Neutrons aux Petits Angles.
- Contributeurs : LLB (~50%), JCNS (~50%)
- Personnels LLB : S. Désert, P. Lavie, A. Chennevière
- Capacités : grande dynamique de vecteurs d’onde (3 ordres de grandeurs simultanés), très petits angles, polarisation, études résolues en temps, environnements échantillons polyvalents.
- Thématiques couvertes : matériaux stimulables, systèmes biologiques, santé, matériaux magnétiques, matériaux pour l’énergies, nano-matériaux, nano-composites, colloïdes et tensio-actifs, systèmes mixtes, …
- Type : diffractomètre non polarisé dédié à l’étude des propriétés structurales (nucléaires et magnétiques) et microstructurales sur poudres (possibilité monocristaux)
- Contributeurs : JCNS (~76%) et LLB (~24%)
- Personnels LLB : S. Désert, B. Annighöfer, G. Fabrèges, F. Porcher
- Capacités : structures nucléaires et magnétiques par diffraction, analyse PDF, (SANS)
- Thématiques couvertes : matériaux pour l’énergie, batteries, matériaux (multi-) fonctionnels, nano-matériaux, magnétisme, supraconducteurs, matériaux zéolithiques et MOFs,…
- Type : spectromètre à géométrie indirecte avec 50 analyseurs/détecteurs couvrant 90° d’angle de diffusion dans le plan horizontal.
- Contributeurs : DTU/KU (~30%), PSI (~27%), LLB (~22%), et IFE (~21%)
- Personnels LLB : S. Rodrigues, P. Lavie, P. Bourges
- Capacités : mesures de diffusion inélastique paramétriques pour l’étude d’excitations magnétiques et de phonons et/ou avec des environnements extrêmes (champ magnétique fort, haute pression,…), haut flux et petits échantillons.
- Thématiques couvertes : matériaux multi-fonctionnels (phonons et magnétisme), supraconductivité, couplage spin-orbite, magnétisme fondamental, magnétisme quantique, matériaux pour l’énergie, thermoélectrique, géologie (haute-pression).
Environnement échantillon
- Aimants et basses températures : aimant supraconducteur à grande ouverture angulaire, aimants supraconducteurs warm-bore, inserts dilution et insert 3He.
- Hautes pressions : cellule liquide/gaz, système de chargement et de mise sous pression et cellule Paris-Edinburgh.
- Personnels LLB : B. Annighöfer, F. Maignen, X. Fabrèges
Instrumentation_ESS 2021-10.pdf