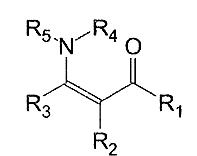
Matériau nanoporeux d’aldéhydes à transduction optique directe
Procédé de détection, dosage ou piégeage d’aldéhyde (préférentiellement le formaldéhyde), par mise en contact d’un flux gazeux avec un matériau comprenant une matrice nanoporeuse sol-gel d’oxydes métalliques. Cette matrice contient une molécule sonde portant une fonction réactive avec la fonction aldéhyde. le brevet porte sur le matériau, sa mise en œuvre, son procédé de préparation, et les capteurs intégrant ces matériaux.
Nanoporous direct optical transducing material for detecting aldehydes
(lien WIPO)
The invention concerns a method for detecting and/or testing and/or capturing at least one type of aldehyde, preferably formaldehyde, consisting in bringing a gas stream into contact with a material comprising a nanoporous metal oxide sol-gel matrix, which contains at least one probe molecule exhibiting at least one reactive function reacting with at least one aldehyde function. A material for carrying out said method, a method for producing the inventive material and sensors integrating said materials are also disclosed.
Contact: T.H. Tran-Thi