Burkhard Annighöfer, Arnaud Hélary, Annie Brûlet, Alexandre Colas de la Noue, Camille Loupiac, and Sophie Combet
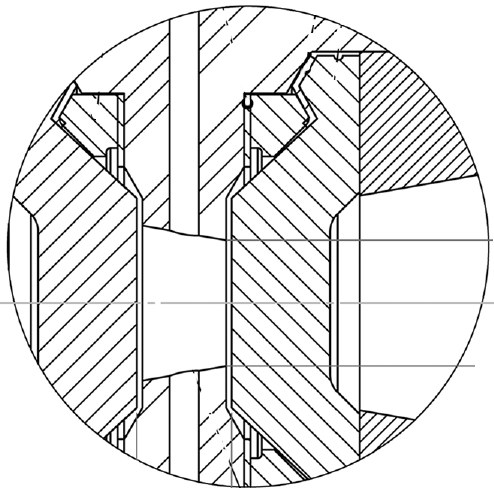
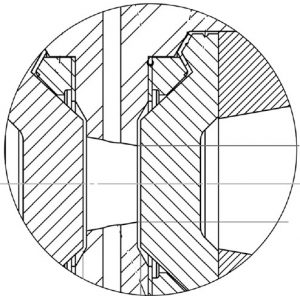
We report on a high pressure (HP) cell designed for the determination of the structure of molecular solutions by small-angle neutron scattering (SANS). The HP cell is fitted up with two thick metallic windows that make the device very resistant under hydrostatic pressures up to 600 MPa (or 6 kbar). The metallic windows are removable, offering the possibility to adapt the HP cell to a given study with the pressure desired on an appropriate spatial range to study the structure of various molecular solutions by SANS. In this context, we report the absorption, transmission, and scattering properties of different metallic windows. Finally, we describe, as a proof of principle, the solution structure changes of myoglobin, a small globular protein.
https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5051765