Objective
One of the biggest limitations of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) is its lack of sensitivity linked to the low nuclear spin polarization. For several years we develop in the lab an optical pumping experiment designed to produce hyperpolarized noble gases. However the out-of-equilibrium character of the hyperpolarization limited us to use the hyperpolarized gases in our NMR spectrometers or in nearby NMR imagers.
The goal of the present project is to produce hyperpolarized gases near the areas of use. For that spin-exchange optical pumping is performed in a van, in close proximity to hospitals or research laboratories. Only compressed air and alternative current need to be supplied by the host laboratory.
Setup
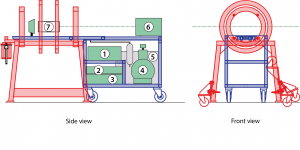
The coils are separated from the rest of the setup. With this principle, it becomes possible by keeping only the latter part to use the fringe field of a horizontal MRI magnet to perform in situ optical pumping simultaneous to MRI. The optical pumping cell is placed on a retractable plateau: while in the transport mode it is in tucked position, it is extended to reach the center of the coils during operation. Both parts are equipped with wheels.

Installation in a van
Both parts of the device can be easily transported to the interior of a van equipped with a power liftgate.
In addition to the SEOP setup, during operation the van compartment contains two chariots and a mobile air conditioning. One of these chariots supports the nitrogen and helium gas bottles, both equipped with manometer and pressure reducer), the second one is a home-built chariot for the transport of polarized xenon. On this chariot, xenon is frozen in a glass coil inside a solenoid immersed in liquid nitrogen. The cold solenoid, electrically supplied by a car battery, delivers a magnetic field of 5 kG. Although no precise measure was done, the xenon relaxation in these conditions is on the order of hours.

For sake of safety during the travel all the devices (the heating system, the electric supply, the pumping group and the laser diode unit) are fixed on the aluminum frame through rivets or bolts.
Working with Class IV lasers in a van requires some adjustments. For safety reasons, the rear doors of the van cannot be closed during operation (in case of emergency no fast exit would be possible). But to protect people from outside of the van to accidentally receive a laser beam reflection, a removable wall in wood is added. This wall contains a door, two electric outlets and a passage for the warm air exhaust.
And it works perfectly, very promising results have already been obtained in CBM Orléans !
C. Chauvin et al., Review of Scientific Instruments 87 (2016) 016105.