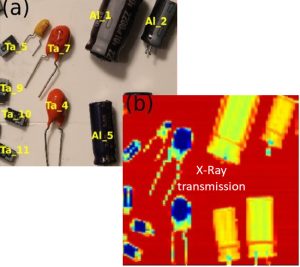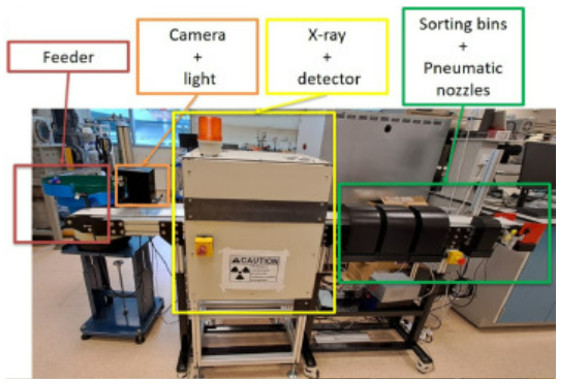
Automatic sorting tool based on computer vision and multi-energy X-rays. Chem. Eng. J. 441, 135886 (2022)
Microfluidics platform combining a microfluidic chip, infrared and X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy for the study of hydrometallurgical processes. Nano Sel. 3, 425 (2022)
Main contacts: Jean-Christophe Gabriel, Guillaume Zante
Recycling
The decarbonization and digitization of the economy is accompanied by a sharp increase in the consumption of metals (lithium, cobalt, copper, niobium, etc.), as well as by an important production of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE).
As part of the SCARCE joint laboratory (CEA/NTU Singapour), multiple processes have been developed to recycle strategic metals from WEEE, in particular those with low recycling rates (tantalum, rare earths, etc.). The use of artificial intelligence coupled with multi-energy X-ray analysis has enabled the development of a unique sorting tool, capable of enriching waste streams with strategic metals by sorting electronic components from WEEE.
The development of hydrometallurgical metal purification processes is facilitated by the laboratory’s microfluidic platform, which combines infrared and X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy to study separation processes (liquid-liquid extraction, ion exchange resins, membrane processes, etc.). The laboratory is also interested in 2D materials and their integration for improved membrane processes.
See the recycling laboratory page.
Further reading: “New technologies to recycle electronic waste” (article in The Conversation) / Fait-Marquant Iramis 2022 (in French) / Fait-Marquant Iramis 2020 (in French)
Gas and water filtration
With our partners at Université Paris-Saclay and the startup AJELIS, we develop polymer fiber materials with advanced capabilities for water depollution, industrial liquid-wastes depollution, rare-earth and metal recovery, air and toxic gas filtration…
Further reading: Discover the company AJELIS / “Procédé SOLIEX : une rupture technologique pour traiter les effluents” (in French) / Brevet Nanofibres