Feb 16, 2024
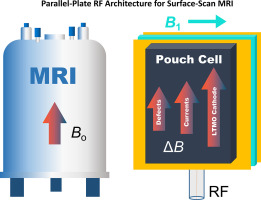
MRI (based on Nuclear Magnetic Resonance - NMR)* is a well-known imaging and analysis method used in medicine for clinical diagnosis. The technique is also widely used in chemistry, biology and the study of materials.
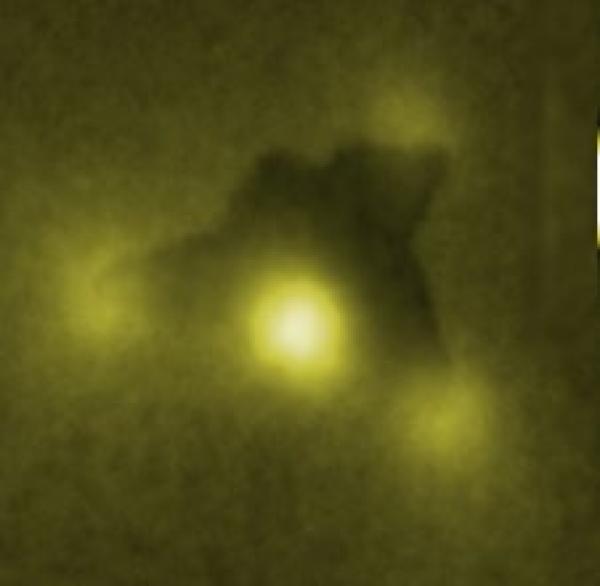
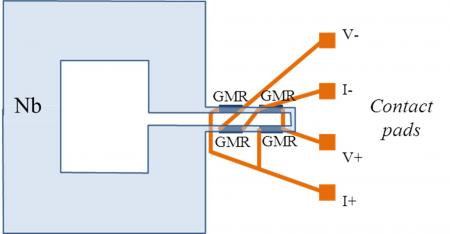
A new method, recently developed and based on MRI, explores the local surface magnetization of an object. Applicable to the study of electrochemical processes, the method can be used to improve electricity storage devices for mobile equipments.
Jul 11, 2022
Version française.
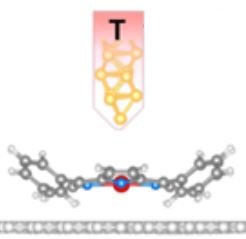
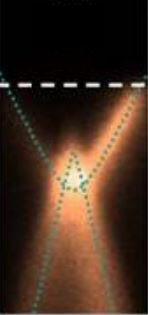
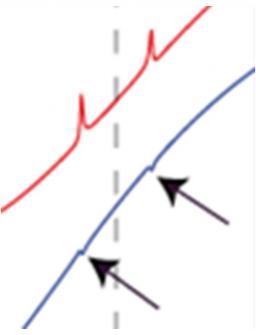
Knowing how to manipulate at the nanometric scale, a single spin, as an object carrying quantum information, presents a major technological challenge, and still remains a subject of great fundamental interest.
Feb 27, 2022
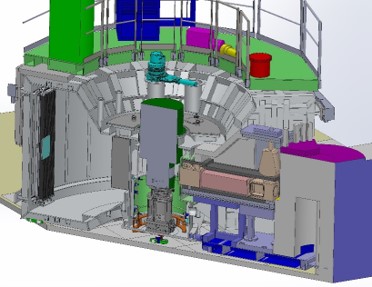
The objective of the realization of efficient compact neutron sources is to make it possible to perform neutron scattering experiments, with practically the same qualities as those carried out with neutron beam lines from research reactors of the Orphée type*.
These compact sources are obtained from a protons beam of medium-energy (3-50 MeV) and high current (100 mA) impinging on a light element target as beryllium. This interaction creates a neutron emission.
Apr 05, 2021
In the Léon Brillouin Laboratory (LLB), and for the community of neutron scattering, this month of March 2021 was marked by an important event: the first neutron beam of the SHARP* instrument, a new time-of-flight neutron spectrometer, at the European reactor of the Institut Laue Langevin (ILL) in Grenoble.
Nov 18, 2020
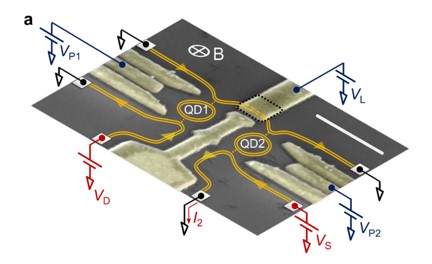
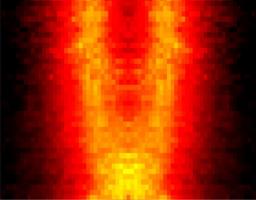
Researchers from SPEC (in collaboration with the C2N and the University of Genoa) have observed the fading and partial reappearance of an electron injected at a finite energy into chiral one dimensional electronic channels propagating along the edges of a two dimensional electron system. These results will help elucidating to which extent these electrons can be used to implement the electronic analogues of quantum information experiments done with photons.
Apr 28, 2020
Black phosphorus (BP) is a stack of monoatomic layers of phosphorus, bound together by Van der Waals forces. This 2d material is today attracting a great interest due to its widely tunable band gap, depending on the thickness of the material, the very high mobility of its carriers, for its application in field effect transistors (FETs), and the possible emergence of topologically protected states.
Dec 13, 2019
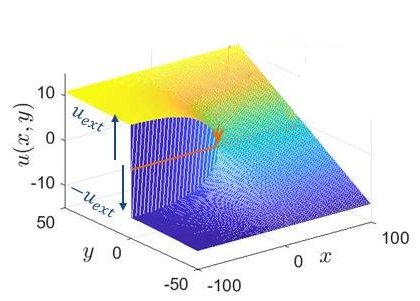
La ténacité d’un matériau définit sa résistance à rupture. Si on sait la mesurer expérimentalement de manière précise, on ne sait pas, à l’heure actuelle, prévoir sa valeur à partir de la structure atomistique du matériau considéré, même dans les cas les plus simples.
Mar 11, 2019
La métrologie (spectroscopie, mesures de temps ou de distances) ou encore la réalisation de réseaux optiques quantiques nécessitent des sources de photons uniques efficaces. Une équipe du SPEC à Saclay, en collaboration avec l'IQST d'Ulm en Allemagne, démontre expérimentalement une voie originale pour obtenir une source de photons microonde uniques, simple, efficace et brillante.
May 16, 2017
Les nanoparticules de métaux nobles présentent d’étonnantes propriétés optiques accessibles à tout un chacun au travers des couleurs chatoyantes des vitraux médiévaux.
Mar 01, 2017
Femto-ARPES observation of the dynamic closure of the superconducting gap in high Tc supraconductors
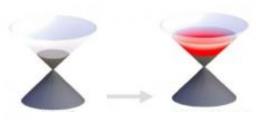
The discovery of superconductivity is more than 100 years old, and the BCS theory, describing the phenomenon in its conventional version, is now 60. Today, the mechanism at the heart of the "high temperature" superconductivity (non BCS), discovered 30 years ago, remains to be identified.
Feb 18, 2017
The chemical bonding in actinide compounds is usually analysed by inspecting the shape and the occupation of the orbitals or by calculating bond orders which are based on orbital overlap and occupation numbers. However, this may not give a definite answer because the choice of the partitioning method may strongly influence the result possibly leading to qualitatively different answers.
Feb 17, 2017
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful tool for biology, allowing structural and chemical analysis of metabolites as well as imagery (MRI). A collaboration of scientists from Nimbe, Neurospin and Bordeaux University, has recently designed a non-invasive online NMR μ-probe for profiling in-vivo metabolic physiological activities with a micro-size NMR detector placed in "close proximity" to a microdialysis sampling probe.
Dec 30, 2016
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a powerful but poorly sensitive analytical technique. Major challenges in chemical analysis (the detection of products in very low concentrations or study of isotopic effects, for instance) encourage to explore new approaches to detect and separate weak signals from the main component ones.
Apr 07, 2016
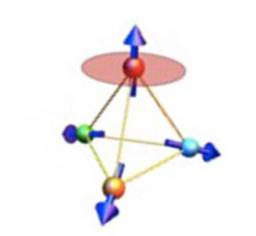
Fractionalized excitations that emerge from a many-body system have revealed rich physics and concepts, from composite fermions in two-dimensional electron systems, revealed through the fractional quantum Hall effect, to spinons in antiferromagnetic chains and, more recently, fractionalization of Dirac electrons in graphene and magnetic monopoles in spin ice.
Mar 25, 2016
Le stockage des déchets radioactifs à vie longue est un des enjeux majeurs de la filière nucléaire. Pour ce faire, les éléments radioactifs sont vitrifiés, au sein d'une matrice de verre placée dans un conteneur en acier. Il est ainsi nécessaire de comprendre la dégradation du verre en présence des produits de corrosion de l'enveloppe métallique.
Sep 02, 2015
Les nouvelles technologies permettant de stocker ou transmettre de l'information sont en plein essor.
Mar 04, 2015
Cooperation between research teams from the CEA, the CNRS and the Université Paris-Sud[1] has resulted in research showing that chemistry tools subjected to radiation make it possible to study the ageing of electrolytes in lithium-ion accumulators. In particular, accelerated ageing can be produced in electrolytes for the purpose of facilitating studies of their life span. This research was published in Nature Communications on 24 April 2015.
May 16, 2014
One of the goals in physical chemistry is to follow reaction paths in details. Many techniques have been developed with studies conducted in cells, effusive or supersonic beams, using laser spectroscopy, mass spectrometry etc. as investigation tools.
Mar 21, 2013
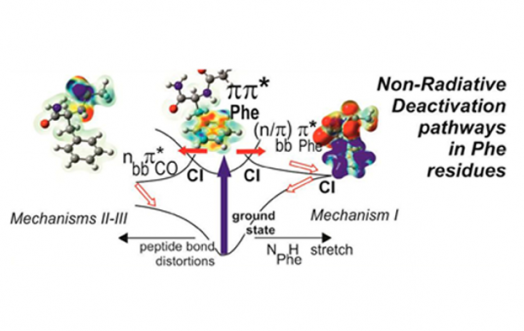
Many complex molecular systems absorb light in the UV spectral range, including those of paramount biological importance, like DNA bases or proteins. The excited states created by UV absorption are endowed with mechanisms of deactivation which are of major importance for the photochemical stability of these species. The majority of these processes are ultrafast and provide a rapid and efficient way to dissipate the electronic energy into vibration, thus avoiding photochemical reactions.
Dec 12, 2012
Ionized molecules are involved in many chemical reactions, and participate for an important part in the chemistry of the upper atmosphere and interstellar clouds. Data on the vibrational spectroscopy of these ions are thus needed to better understand the dynamics and energetics of so diluted matter.
May 31, 2012
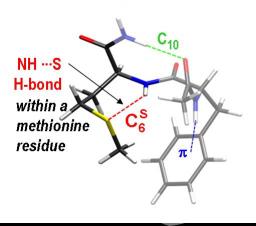
The description of the interactions controlling the shape of a protein is crucial in understanding the cellular mechanisms, but is still difficult to achieve on biological systems because of their complexity.
In this context, the use of model molecules makes accessible to experiments many biological problems lying at the heart of current societal issues. Gas-phase IR/UV spectroscopy of small peptides is an outstanding example.
Nov 23, 2011
K. Katsuyoshi, D. L'Hôte, S. Nakamae, M. Konczykowski, V. Mosser
Le théorème de fluctuation-dissipation, reliant l'intensité des fluctuations d'une observable à la réponse à une sollicitation, est un principe vérifié pour tous les systèmes à l'équilibre thermodynamique.
Sep 24, 2011
Contact CEA : Pascal Boulanger
A decade after their first synthesis in the laboratory, carpets of aligned carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are being considered in many fields of applications (filtration membranes, passive and active electronic components, composite materials,..) combining CNTs’ individual properties and nano-structuration. But the development of these applications requires a safe, inexpensive process that is applicable over large areas.
Jul 18, 2011
( Version française)
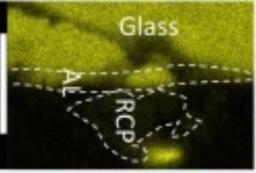
Stress corrosion - combined action of mechanical stress and corrosion by water from the surrounding atmosphere - is often the cause of crack propagation in glasses. A study by neutron reflectivity at the Laboratoire Léon Brillouin (IRAMIS / LLB) of samples of silica glass fractured under an atmosphere of heavy water (D2O) shows a high penetration of water into the glass.
Apr 21, 2011
Jacques Jestin, Nicolas Jouault, Chloé Chevigny, François Boué, Laboratoire Léon Brillouin, CEA Saclay
One way to strengthen the mechanical properties of plastic materials is to add nanoparticles, forming that way a composite material. A detailed structural study by neutron scattering, coupled with mechanical tests, of polystyrene reinforced with silica particles has been performed at the Laboratoire Léon Brillouin (LLB) at CEA Saclay. It shows the importance to control the concentration and distribution of particles entering in the composition of the material.
Apr 19, 2011
Measurement of the cardiac electrical activity allows following the heart dynamics. Usually measured with electrodes during an electrocardiogram (ECG), this activity can also be studied by monitoring the magnetic component, induced by the circulation of the heart electric currents. This is called "magnetocardiography (MCG).
Feb 15, 2011
Jérôme Polesel Maris, José Moran Meza, Christophe Lubin, François Thoyer, Jacques Cousty
Les chercheurs du SPCSI viennent de mettre au point un nouveau microscope à sonde locale permettant la caractérisation fine des couplages mécano-électriques d’édifices moléculaires. Cet appareil, combinaison d'un STM et d'un AFM, est basé sur un capteur intégré piézoélectrique maintenu en oscillation à sa fréquence de résonance.
Jan 30, 2011
In collaboration with chemists of ENS Lyon and biophysicists of DSV (IBiTeC-S), a team of LSDRM (IRAMIS/SIS2M) designed a cellular probe taking advantage of the extreme sensitivity of NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) of hyperpolarized xenon*. The experiment shows the excellent selectivity of the method to detect the chosen molecular target .
Jan 27, 2011
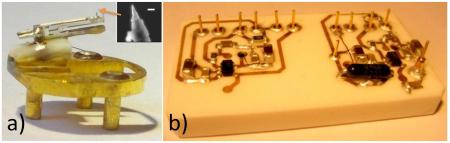
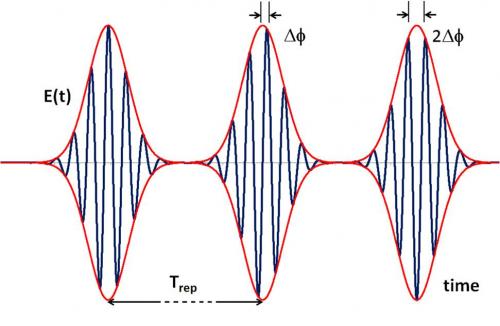
One of the key research topic in the field of ultra-short laser pulses (femtosecond: 10-15 s) is the stabilization of the position of the carrier envelope (called CEP for "Carrier Envelope Phase"). An innovative device to control CEP fluctuations is offered by the CEA/SLIC (Saclay Laser-matter Interaction Centre) in collaboration with the Amplitude Technologies Company (AT).
Nov 24, 2010
C. Hrelescu, T. K. Sau, A. L. Rogach, F. Jäckel, G. Laurent, L. Douillard et F. Charra
In optics, the possibility to confine light below its natural wavelength is hampered by the longstanding barrier of the diffraction limit. Surface plasmons are electromagnetic surface waves coupled to free electrons at metal dielectric interfaces. They offer a unique opportunity for scaling down photonic devices to the nanometre range.