M. Deutsch, W. Peng, P. Foury-Leylekian, V. Balédent, S. Chattopadhyay, M. T. Fernandez-Diaz, T. C. Hansen, A. Forget, D. Colson, M. Greenblatt, M.-B. Lepetit, S. Petit, and I. Mirebeau
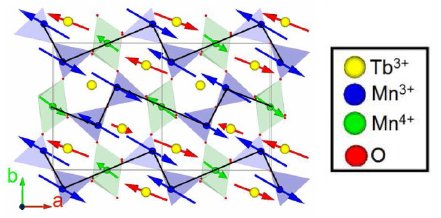
The magnetic structure of TbMn2O5 and DyMn2O5 multiferroics has been studied by high-pressure neutron diffraction in a large pressure range up to 6.6 GPa. In both cases, we observe a pressure-induced commensurate magnetic phase with propagation vector ( 1/2 0 1/2 ), growing with pressure at the expense of the ambient pressure phases. Being previously observed in YMn2O5 and PrMn2O5, this phase is most likely a generic feature of the RMn2O5 multiferroic family. A simple model is proposed to explain qualitatively the emergence of this pressure-induced phase. Differences between TbMn2O5 and DyMn2O5 behaviors at ambient and low pressures provide clues on the interaction scheme.
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.98.024408