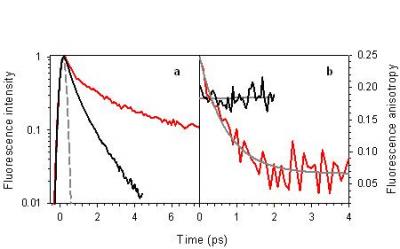
DNA nanostructures formed by association of four oligonucleotides d(TGGGGT) (TG4T quadruplexes) are studied by steady-state and time-resolved optical spectroscopy with femtosecond resolution using fluorescence upconversion. A comparison between single-stranded and four-stranded structures and the corresponding stoichiometric mixture of non-interacting nucleotides shows how horizontal and vertical organization affects the properties of the excited states. Emission from guanine excimers is observed only for single strands, where conformational motions favor their formation. Quadruplex fluorescence arises from a multitude of excited states generated via electronic coupling between guanines; the average fluorescence lifetime is longer and the fluorescence quantum yield higher compared to those of non-interacting nucleotides. The fluorescence anisotropy recorded on the sub-picosecond time-scale, where molecular motions are hindered, reveal that energy transfer takes place among the bases composing the nanostructure. These results are in line with the conclusions drawn from similar studies on model DNA duplexes.
Franois-Alexandre Miannay, Akos Banyasz, Thomas Gustavsson and Dimitra Markovitsi
J. Phys. Chem. C, 113 (27) (2009) 11760.
•  Physique et chimie pour le vivant et l’environnement › Physique et vivant / Physics and life
Physique et chimie pour le vivant et l’environnement › Physique et vivant / Physics and life
• IRAMIS: Saclay Institute of Matter and Radiation • Service des Photons Atomes et Molécules • Service des Photons Atomes et Molécules