13 décembre 2019
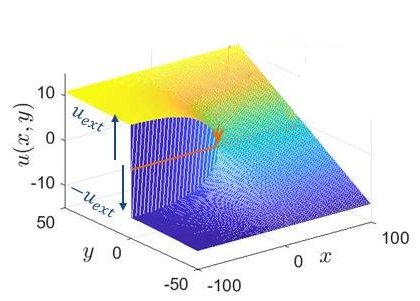
La ténacité d’un matériau définit sa résistance à rupture. Si on sait la mesurer expérimentalement de manière précise, on ne sait pas, à l’heure actuelle, prévoir sa valeur à partir de la structure atomistique du matériau considéré, même dans les cas les plus simples.
11 mars 2019
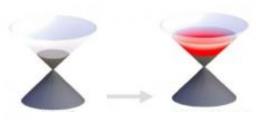
La métrologie (spectroscopie, mesures de temps ou de distances) ou encore la réalisation de réseaux optiques quantiques nécessitent des sources de photons uniques efficaces. Une équipe du SPEC à Saclay, en collaboration avec l'IQST d'Ulm en Allemagne, démontre expérimentalement une voie originale pour obtenir une source de photons microonde uniques, simple, efficace et brillante.
16 mai 2017
Les nanoparticules de métaux nobles présentent d’étonnantes propriétés optiques accessibles à tout un chacun au travers des couleurs chatoyantes des vitraux médiévaux.
18 février 2017
The chemical bonding in actinide compounds is usually analysed by inspecting the shape and the occupation of the orbitals or by calculating bond orders which are based on orbital overlap and occupation numbers. However, this may not give a definite answer because the choice of the partitioning method may strongly influence the result possibly leading to qualitatively different answers.
25 mars 2016
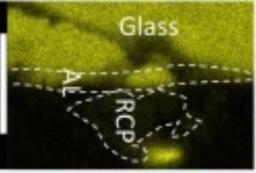
Le stockage des déchets radioactifs à vie longue est un des enjeux majeurs de la filière nucléaire. Pour ce faire, les éléments radioactifs sont vitrifiés, au sein d'une matrice de verre placée dans un conteneur en acier. Il est ainsi nécessaire de comprendre la dégradation du verre en présence des produits de corrosion de l'enveloppe métallique.
02 septembre 2015
Les nouvelles technologies permettant de stocker ou transmettre de l'information sont en plein essor.
23 novembre 2011
K. Katsuyoshi, D. L'Hôte, S. Nakamae, M. Konczykowski, V. Mosser
Le théorème de fluctuation-dissipation, reliant l'intensité des fluctuations d'une observable à la réponse à une sollicitation, est un principe vérifié pour tous les systèmes à l'équilibre thermodynamique.
15 février 2010
Chemists of DSV (CEA-Life science Division) and physicists of DSM (CEA-Matter science Division) specialists of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) have developed a new solid state NMR apporach to measure long inter-atomic distances. Based on the use of tritium, the hydrogen isotope with the highest sensitivity to NMR, this technique allows the determination of the conformation of small molecules bounded to their biological receptors.
15 juillet 2008
D. Bonamy and L. Ponson (SPCSI), D. Santucci (Fysik Institutt Oslo)
Fracture is a phenomenon of everyday life: it is observable at all scales of condensed matter, from the atomic scale (in nanostructures) to the scale of our planet marked by fractures in the continental plates. But, can we find a unifying model to describe the phenomenon?
The dynamics of fracture is complex.
16 avril 2008
Delphine Lebeugle, Dorothée Colson, Anne Forget, Michel Viret (IRAMIS/SPEC CEA-Saclay) Arsen Goukassov, Alexandre Bataille (IRAMIS/LLB CEA-Saclay)
Magnetic materials are heavily used in the dynamic storage of information (hard disk drive, head for reading). For these applications, they are most often designed in the form of thin films. This was achieved after the birth of the spin electronics or "spintronics" and the discovery of the giant magnetoresistance.