Pages scientifiques 2017
1. HR-MAS of micro-scale specimens
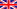
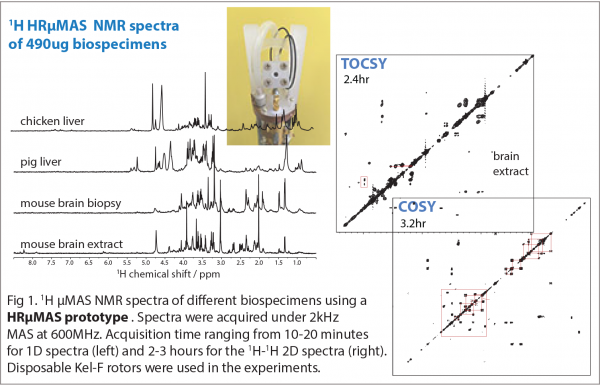
1H HRMAS (High-Resolution Magic-Angle Spinning) NMR spectroscopy has found success in the study of metabolome in heterogeneous biospecimens, such as cells, tissues and orgamis, owing to its sample non-destructive nature and simplicity data aquisition. However, NMR in general is an insensitive spectroscopic technique relying on large sample quantity, typically 10-20 mg per spectral data; and it has limited the metabolic invertigations in biology and in medicine. For this reason, there is presently a need to develop new NMR methodologies that are capable for analyzing small-scale specimens. One approach is the use of a micro-size detection under MAS condition, but unlike the standard uMAS commerical probe, it must offers high detection sensitivity without compromising the spectral resolution (i.e., <0.002ppm). Here, we are developing a HR-MAS methodology capable of offering excellent spectral quality in sensivity and resolutoin for metabolic applications.
References:
'Evaluation of a high-resolution micro-size magic angle spinning (HRuMAS) probe for NMR-based metabolic studies of nanometer samples'
N. T. Duong, Y. Endo, T. Nemoto, H. Kato, A-K Bouzier-Sore, Y. Nishiyama, A. Wong, Anal. Methods 8 (2016) 6815-6820.
'High-resolution NMR-based metabolic detection of microgram biopsies using a 1 mm HRuMAS probe'
Y. Nishiyama, Y. Endo, T. Nemoto, A-K Bouzier-Sore, A. Wong. Analyst 140 (2015) 8097-8100.
Financial Supports:
- ANR-PRC (2016-2019) on HRuMAS.
- ANR-JCJC (2012-2015) : Développement et exploration de nouveaux micro-détecteurs RMN tournants pour des analyses métabolomiques de biopsies de petite masse – HRMACS