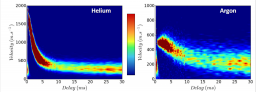
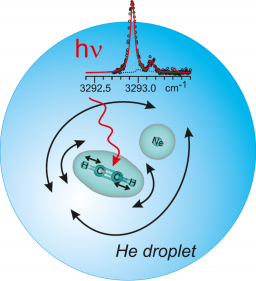
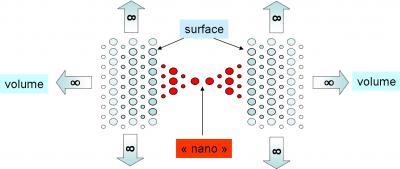
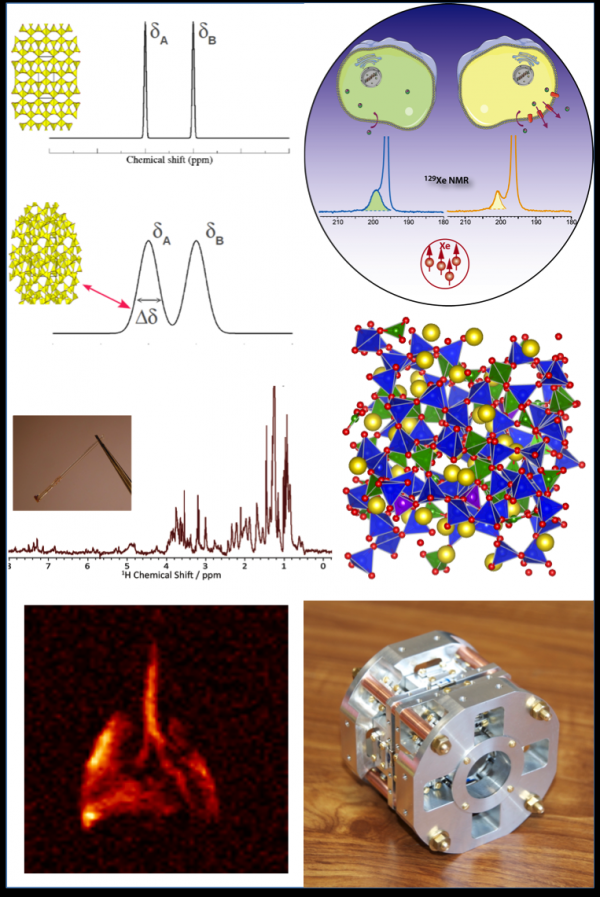
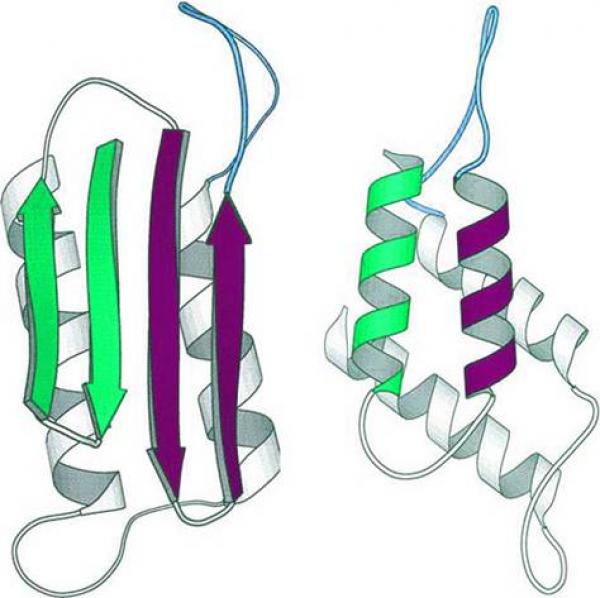
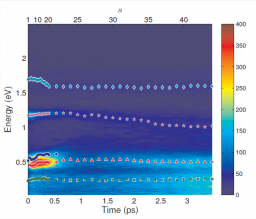
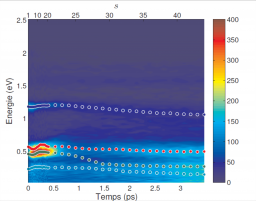
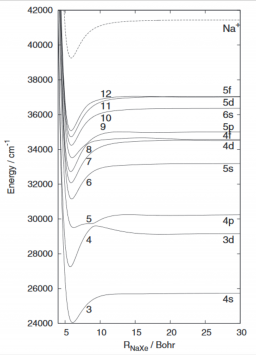
Institut Rayonnement Matière de Saclay
Institut Rayonnement Matière de Saclay
L’Institut Rayonnement-Matière de Saclay (IRAMIS) est un des principaux instituts de la Direction de la Recherche Fondamentale (DRF) du Commissariat à l'Energie Atomique et aux Energies Alternatives (CEA). L’IRAMIS comprend six unités mixtes de recherche, en association avec le CNRS, l'École Polytechnique ou ENSICAEN. Quatre sont situées sur le Centre de Saclay (LIDyL, LLB, NIMBE et SPEC), membre de l'Université Paris-Saclay, une sur le site de l’Ecole Polytechnique (LSI) et une à Caen (CIMAP), auprès du GANIL.
Parcourez l'IRAMIS : - par thème de recherche - par Unité - par technique
Les recherches en physique et en chimie qui y sont menées sont en lien étroit avec les enjeux sociétaux et les programmes du CEA :
- Nanosciences pour les technologies de l'Information et de la Santé (RF-TIS)
- Interaction rayonnement-matière, autour des grandes infrastructures de recherche
- Énergies bas carbone
Pour conduire ces recherches, les équipes de l’IRAMIS mettent en œuvre des installations et équipements scientifiques de premier plan et sont aussi très actives autour des Grands Instruments Européens.
Les recherches, principalement de nature fondamentale, menées à l’Institut sont ouvertes sur la création de valeur économique et le transfert technologique. L'IRAMIS est aussi présent dans 4 LABEX et 4 EQUIPEX du programme d'Investissement d'Avenir du gouvernement français.
 Site WEB : http://iramis.cea.fr/
Site WEB : http://iramis.cea.fr/