PAPYRUS

"PETITS ANGLES POLARISES A L'USAGE DES SURFACES"
"small angle and grazing incident polarised neutrons
for surfaces (and interfaces)"
Technical specifications
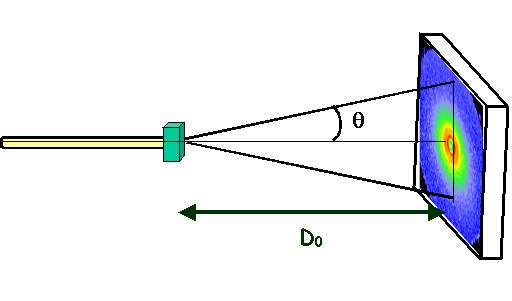
Accessible Q-range in SANS configuration
maximum angle = 17.7o (D=1 m)
= 4.57o (D=4 m)
D0=1 m 0.008 Å-1 < Q < 0.24 Å-1
D0=4 m 0.002 Å-1 < Q < 0.06 Å-1
Accessible Q-range in Reflectivity configuration
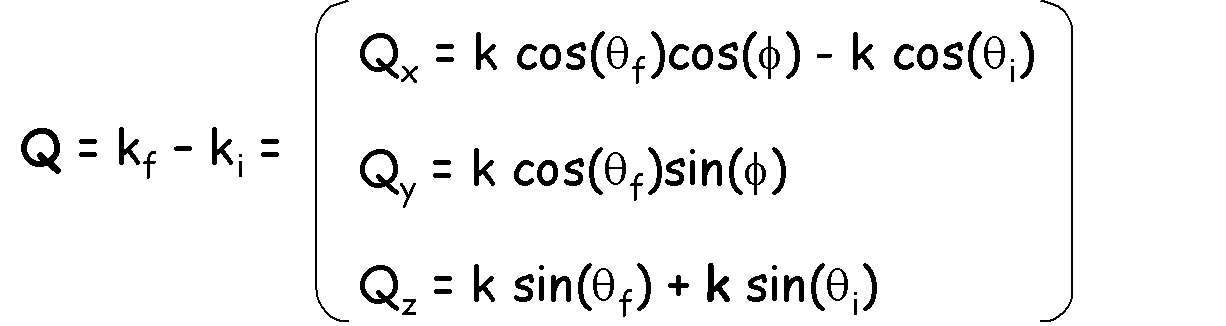

Visualisation and data treatment softwares
Refer to Simulations and Fitting programs on the PRISM web page (SpectraProcessor, SimulReflec, etc.)
Information on the spectrometer

Displex ARS (range 4-300K)
GMW electro-magnets (range 0 - 15kG in H transverse to ki mode, 0 - 1kG in H parallel to ki mode.
More information here (.doc file).
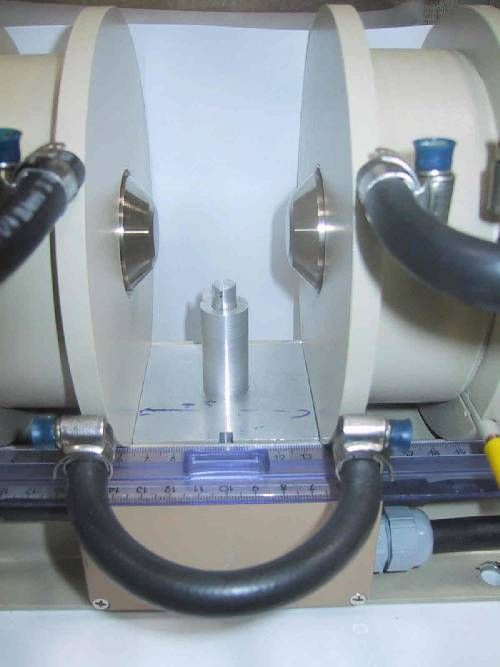

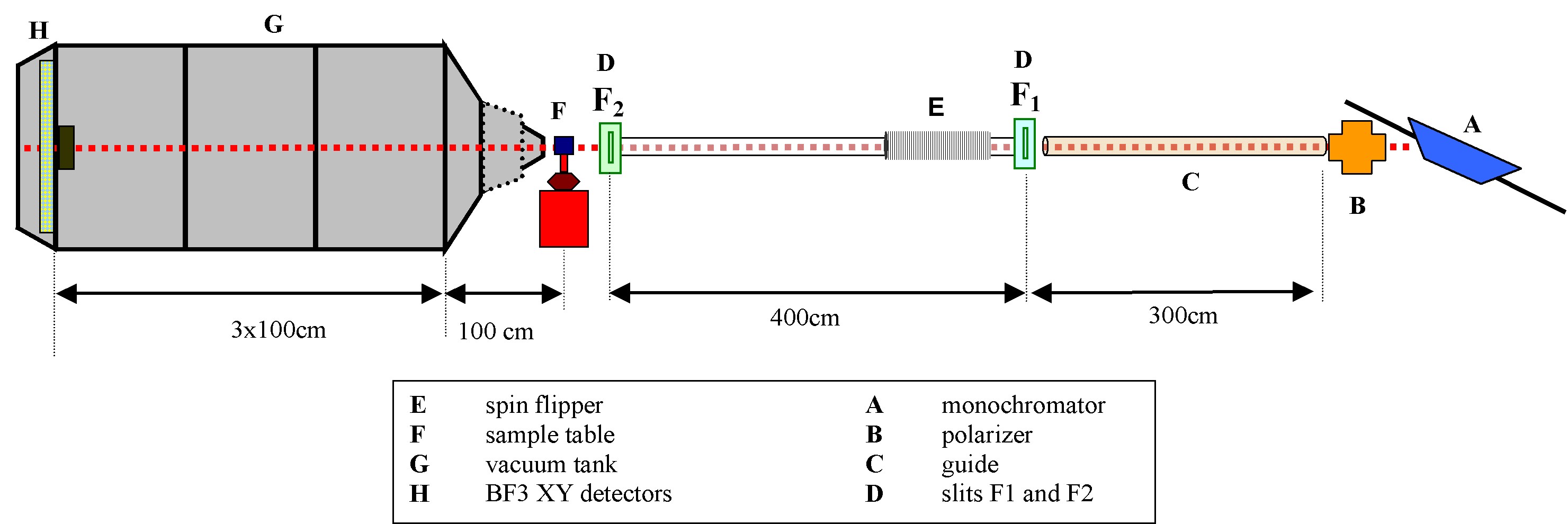
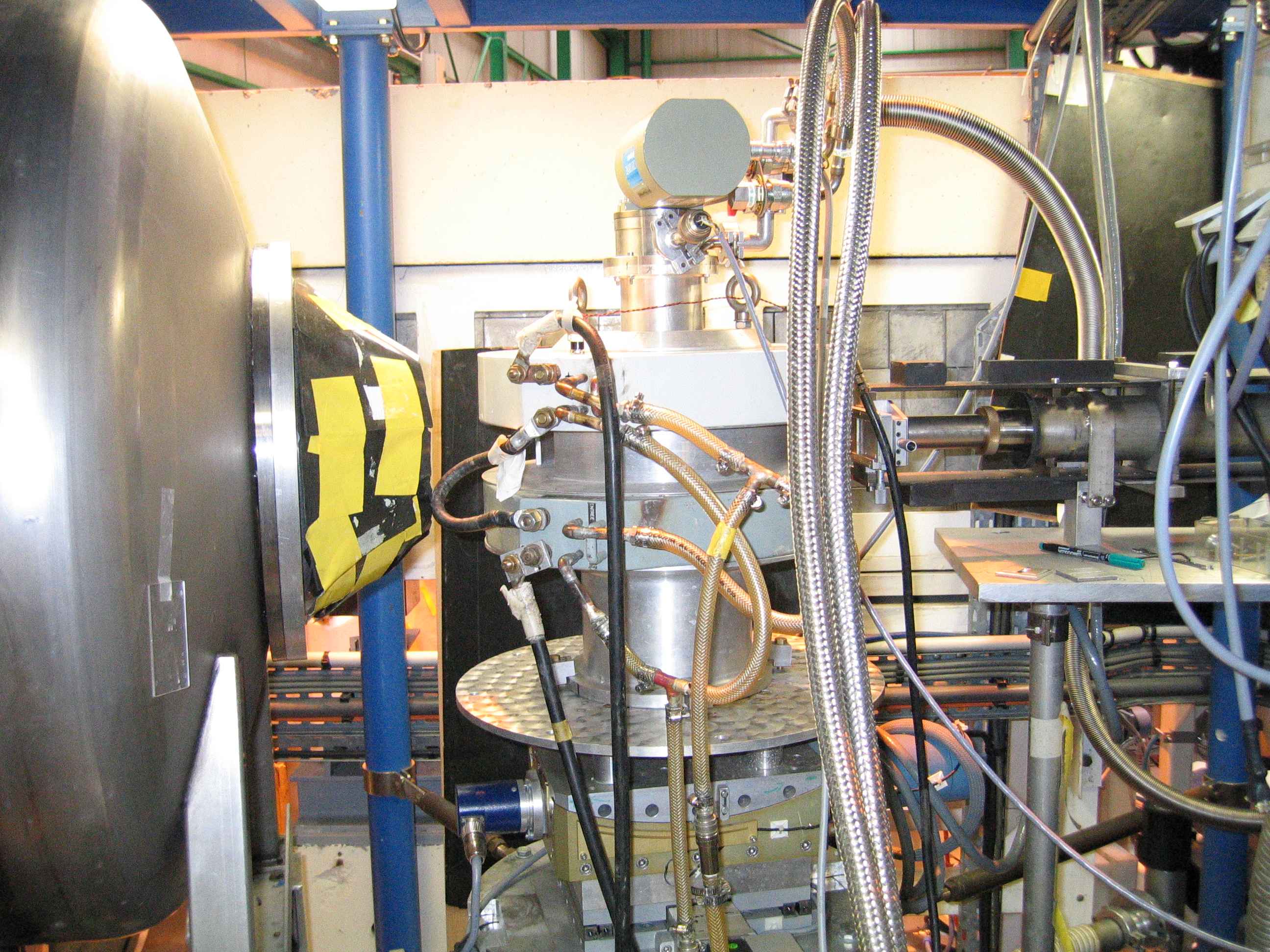
Detector tank
The lenght of the detector tank is ajustable from 1m to 4m by chunks of 1m. To maximise transmission, the tank is under vacuum. The direct beam is blocked before hitting the detcctors by an absorber (Cadmium plate).
The neutron detection is obtained by an XY BF3-type detector. The detection coverage is 64x64 cm and each cell is 0.5x0.5cm (128x128 pixels).

Miscellaneous
Bibliography
S.J. Blundell and J.A.C. Bland, Physical Review B 46, pp. 3391 (1992).
"Polarized Neutron Reflection as a Probe of Magnetic Films and Multilayers."
S. Dietrich and A. Haase, Physics Reports 260, pp. 1-138 (1995).
"Scattering of X-Rays and Neutrons at Interfaces."
G.P. Felcher, R.O. Hilleke, R.K. Crawford, J. Haumann, R. Kleb and G. Ostrowsky, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 58, pp. 609-619 (1987).
"Polarized Neutron Reflectometer: A New Instrument to Measure Magnetic Depth Profiles."
C. Fermon, Physica B 213-214, pp. 910-913 (1995).
"Neutron Reflectometry with Polarization Analysis: A Theory and a New Spectrometer."
Hercules Courses, Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation for Condensed Matter Studies (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1993).
D. A. Korneev, V.I. Bodnarchuk and V.K. Ignatovich, JETP Lett. 63, pp. 944-951 (1996).
"Off-Specular Neutron Reflection From Magnetic Media with Nondiagonal Reflectivity Matrices."
Majkrzak C.F. and Berk N.F., Physical Review B 52 (15), pp. 10827-10830 ( 1995).
"Exact Determination of the Phase in Neutron Reflectometry."
F. Ott and C. Fermon, Physica B 234-236, pp. 522-524 (1997).
"Spin Analysis and New Effects in Reflectivity Measurements."
R. Pynn, Phys. Rev. B 45, pp. 602-612 (1992).
"Neutron Scattering by Rough Surfaces at Grazing Incidence."
V. F. Sears, Neutron News 3 (3) (1992).
"Neutron Scattering Lengths and Cross Sections."
S.K. Sinha, E.B. Sirota, S. GAroff and H.B. Stanley, Physical Review B 38 (4 ), pp. 2297-2311 (1988).
"X-Ray and Neutron Scattering from Rough Surfaces."
S.K. Sinha, Physica B 174, pp. 499-505 (1991).
"Complementary of Neutrons and X-Rays as Probes of Surfaces and Interfaces."
Y. Yoneda, Physical Review 131, pp. 2010-2013 (1963).
"Anomalous Surface Reflection of X-Rays."
H. Zabel, Physica B 198, pp. 156-162 (1994).
"Spin Polarized Neutron Reflectivity of Magnetic Films and Superlattices"

"PETITS ANGLES POLARISES A L'USAGE DES SURFACES"
"small angle and grazing incident polarised neutrons
for surfaces (and interfaces)"
Experiments
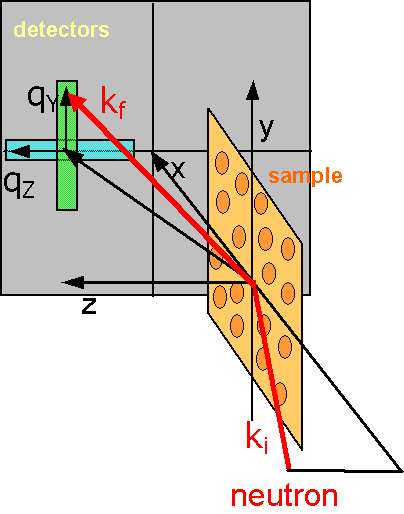
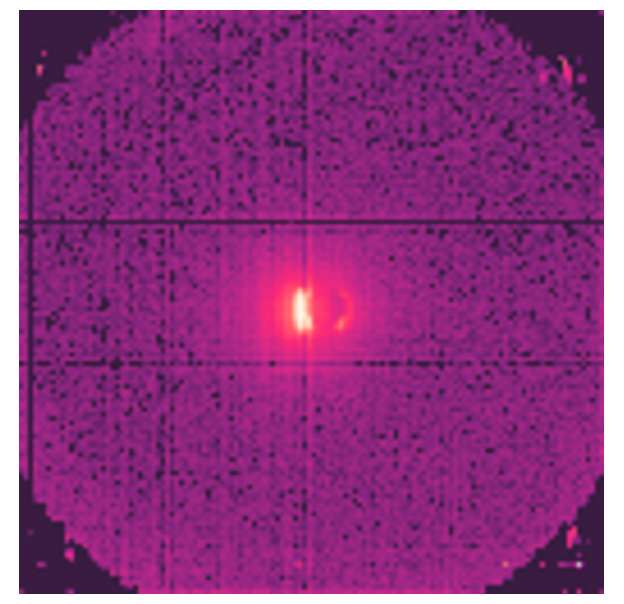
PAPYRUS, formerly PAPOL, is a spectrometer that has been modified to perform Grazing Incidence Small Angle Neutron Scattering (GISANS). It is primarily devoted to the study of surface and interface at the nanometer scale. GISANS (and SANS) can be performed using a 0.8nm wavelength neutron beam with polarization option (94% polarization, 45% transmission). It allows to work in the Q-range 0.02-2.4 nm-1 thanks to a 64x64 cm BF3 detector grid (128x128 cells) and an adjustable sample-to-detectors distance (min=1m, max=4 m). PAPYRUS can also be used as a standard polarised neutron reflectivity instrument, probing structural and magnetic depth profile.
The GISANS configuration, schematically represented above, is particularly useful for the study of domain formation in magnetic thin films, organized nanostructures (nanowires, nanodots) and soft matter materials.
By detecting off-specular scattering perpendicular to the incident plane (qY direction, green area) one can bring information on the lateral (planar) correlations between nanometer scale objects deposited on a surface or confined at interfaces with typical size between 5 and 100 nm.
Off specular scattering in the incident plane (light blue area) also brings information about lateral structures (in the plane of the surface) but with typical length scales from 600nm to 60mm.
PAPYRUS, formerly PAPOL, is a spectrometer that has been modified to perform Grazing Incidence Small Angle Neutron Scattering (GISANS). It is primarily devoted to the study of surface and interface at the nanometer scale. GISANS (and SANS) can be performed using a 0.8nm wavelength neutron beam with polarization option (94% polarization, 45% transmission). It allows to work in the Q-range 0.02-2.4 nm-1 thanks to a 64x64 cm BF3 detector grid (128x128 cells) and an adjustable sample-to-detectors distance (min=1m, max=4 m). PAPYRUS can also be used as a standard polarised neutron reflectivity instrument, probing structural and magnetic depth profile.
The GISANS configuration, schematically represented above, is particularly useful for the study of domain formation in magnetic thin films, organized nanostructures (nanowires, nanodots) and soft matter materials.
By detecting off-specular scattering perpendicular to the incident plane (qY direction, green area) one can bring information on the lateral (planar) correlations between nanometer scale objects deposited on a surface or confined at interfaces with typical size between 5 and 100 nm.
Off specular scattering in the incident plane (light blue area) also brings information about lateral structures (in the plane of the surface) but with typical length scales from 600nm to 60mm.
Technical specifications
- Monochromator Multilayer Ni-Ti on Si
- Fixed wavelength 8 Å ± 0.5
- Polarizer Transmission 45% Polarization 94%
Flat mirrors in reflection
geometry
The polarisation option can be
switched off to run in unpolarized mode.
- Collimation length 7 m fixed (3m guide + 4m collimation)
- Sample to detector distance 1 m to 4 m variable in steps of 1 m
- Area detector 64 x 64 cm, cell size 5x5 mm
- Beam intensity 3.104 n/cm2/s at the sample
- Data acquisition Proprietary, PAXY compatible
- background noise 0.5 counts / cell / hour
- Beam stop motorized cadmium plates (circular, rectangular)
- Equipment and sample environment
Superconducting Horizontal magnet:5T Oxford Instruments split coil
with high homogeneity (5 10-5), horizontal access parallel (diameter 89 mm)
and perpendicular to the field (diameter 42 mm)
Dilution insert to cool the 4He-filled sample holder to T = 0.2 K
and perpendicular to the field (diameter 42 mm)
Dilution insert to cool the 4He-filled sample holder to T = 0.2 K
Accessible Q-range in SANS configuration
maximum angle = 17.7o (D=1 m)
= 4.57o (D=4 m)
D0=1 m 0.008 Å-1 < Q < 0.24 Å-1
D0=4 m 0.002 Å-1 < Q < 0.06 Å-1
Accessible Q-range in Reflectivity configuration

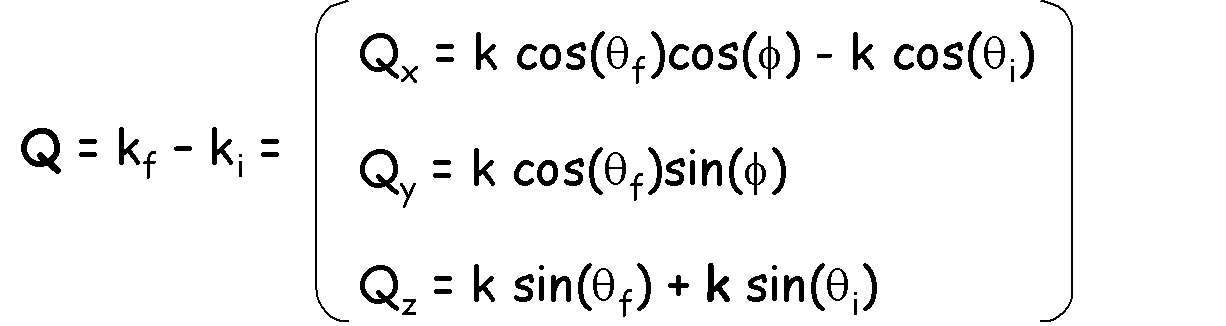

Visualisation and data treatment softwares
Refer to Simulations and Fitting programs on the PRISM web page (SpectraProcessor, SimulReflec, etc.)
Information on the spectrometer
PAPYRUS uses a monochromatic
beam of wavelength 0.8±0.05nm on the lower part of the G5 guide
. The monochromator is a Ni-Ti multilayer on Si substrate. The
polarised neutron beam size is 25x25 mm2. For topological
reasons the detector array is placed outside the vaccum tank. For this
reason, the sample-to-detector distance can only be changed by
increments of 1 m between 1m and 4m.
Polarizer
Adiabatic Flipper
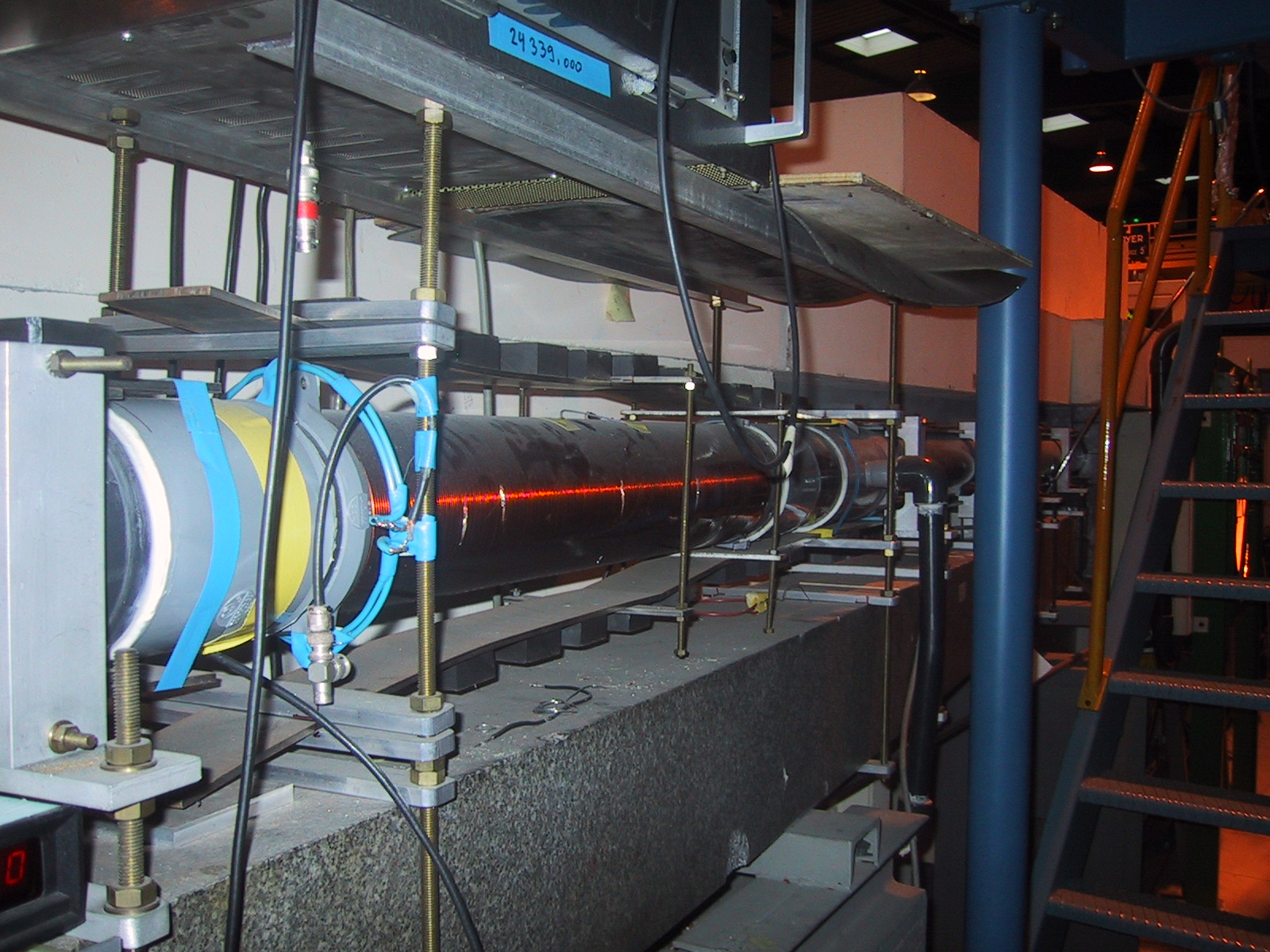
Collimation and slits
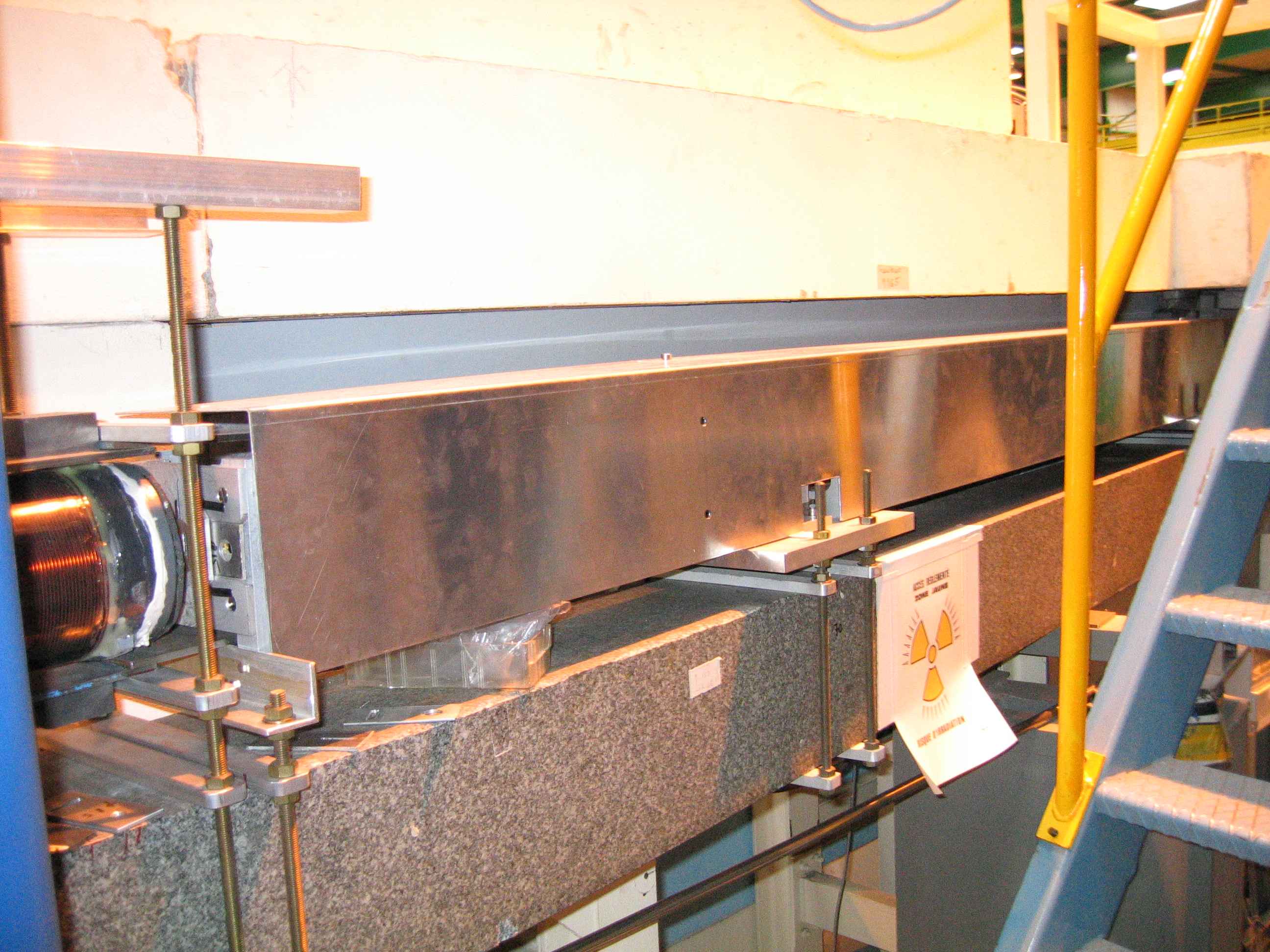

There are two Cadmium slits (F1 and F2) separated by 4m. The first slit F1 is located between the 3m neutron guide and the adiabatic flipper. The F2 slit is right before the sample area. A sliding device allows to adjust the distance bewteen F2 and the sample position according from a few cm up to 30-50cm.
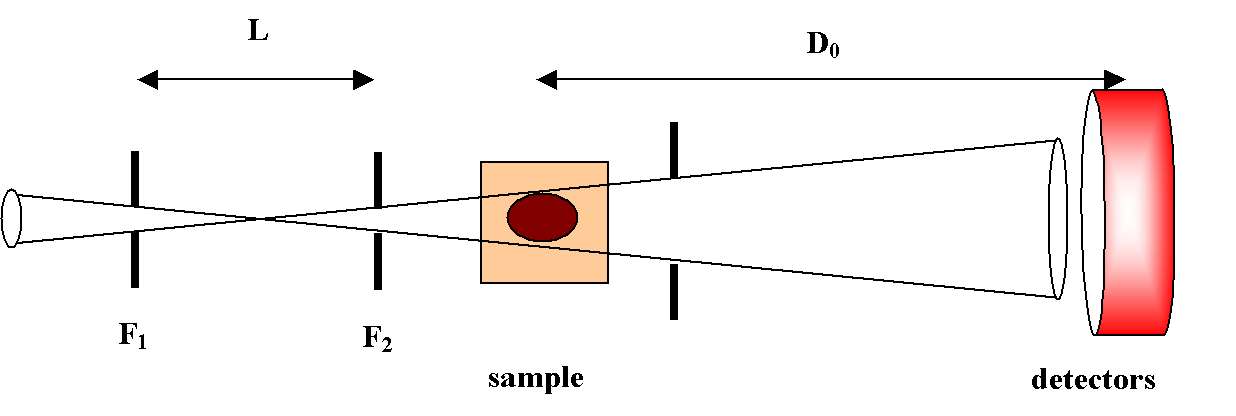
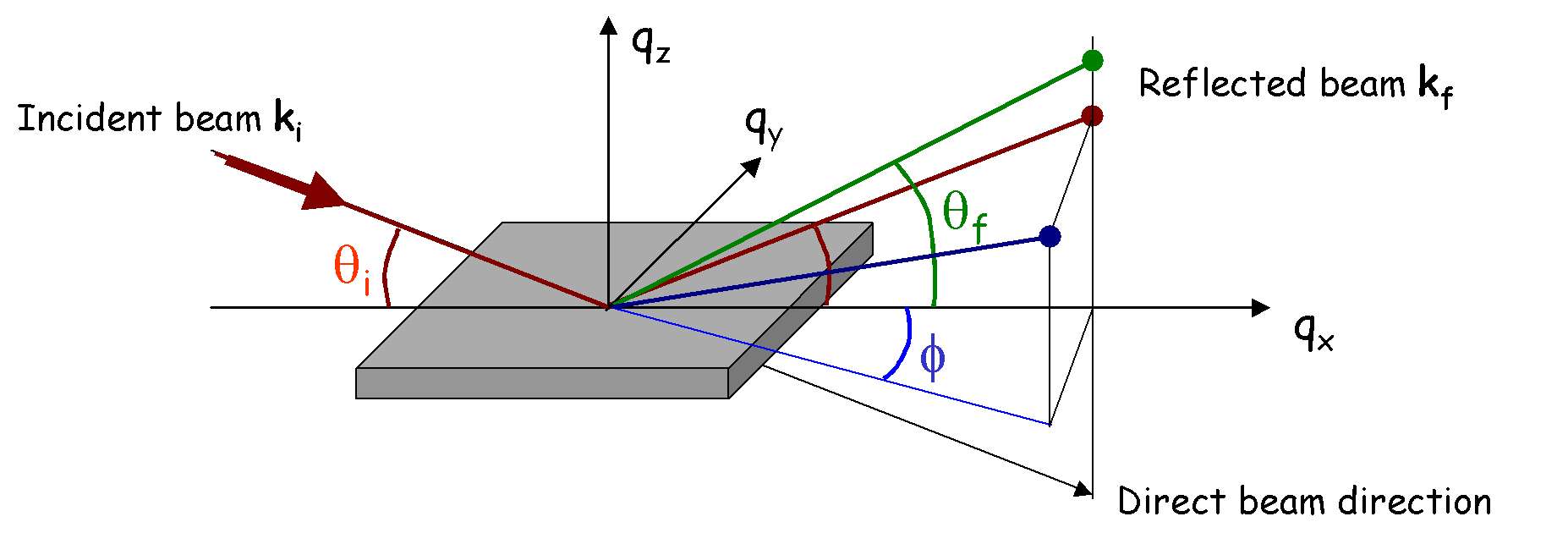
The resolution is, roughly speaking, given by R=(W1+W2)/2L where W1 and W2 are the slits openings and L is the slit separation (see figure)/
For W1=W2=2 mm and L=3 m, we have R=0.04 degrees.
Sample environment
sample table
The sample table allows horizontal motions, like rotation and translation, and vertical motions like tilting and lifting.
Cryostats (range: 0-5T, 2-300K). Field is in the horizontal plane, either longitudinal or transverse to the incident beam.
Adiabatic Flipper
Collimation and slits
De to the improved 7m-long collimation (3m neutron guide) the qZ resolution is labout 0.02 nm-1 and is essentially limited by the resolution of the detector grid.
There are two Cadmium slits (F1 and F2) separated by 4m. The first slit F1 is located between the 3m neutron guide and the adiabatic flipper. The F2 slit is right before the sample area. A sliding device allows to adjust the distance bewteen F2 and the sample position according from a few cm up to 30-50cm.

The resolution is, roughly speaking, given by R=(W1+W2)/2L where W1 and W2 are the slits openings and L is the slit separation (see figure)/
For W1=W2=2 mm and L=3 m, we have R=0.04 degrees.
Sample environment
The sample table area is now motorized in four directions
(vertical, rotation, translation, tilting) and allow accurate
reflectivity measurements as well as GISANS measurements in horizontal
geometry which is the most convenient for liquid samples.
sample table
The sample table allows horizontal motions, like rotation and translation, and vertical motions like tilting and lifting.
Cryostats (range: 0-5T, 2-300K). Field is in the horizontal plane, either longitudinal or transverse to the incident beam.

Displex ARS (range 4-300K)
GMW electro-magnets (range 0 - 15kG in H transverse to ki mode, 0 - 1kG in H parallel to ki mode.
More information here (.doc file).

Sample holders
for displex and low temp
for ambiant conditions
for ambiant conditions
Detector tank
The lenght of the detector tank is ajustable from 1m to 4m by chunks of 1m. To maximise transmission, the tank is under vacuum. The direct beam is blocked before hitting the detcctors by an absorber (Cadmium plate).
The neutron detection is obtained by an XY BF3-type detector. The detection coverage is 64x64 cm and each cell is 0.5x0.5cm (128x128 pixels).

Miscellaneous
conversion factors (meV to THz, etc.)
scattering lengths table (in french)
Papyrus Annual Report 2004 (Word document)
scattering lengths table (in french)
Papyrus Annual Report 2004 (Word document)
Bibliography
S.J. Blundell and J.A.C. Bland, Physical Review B 46, pp. 3391 (1992).
"Polarized Neutron Reflection as a Probe of Magnetic Films and Multilayers."
S. Dietrich and A. Haase, Physics Reports 260, pp. 1-138 (1995).
"Scattering of X-Rays and Neutrons at Interfaces."
G.P. Felcher, R.O. Hilleke, R.K. Crawford, J. Haumann, R. Kleb and G. Ostrowsky, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 58, pp. 609-619 (1987).
"Polarized Neutron Reflectometer: A New Instrument to Measure Magnetic Depth Profiles."
C. Fermon, Physica B 213-214, pp. 910-913 (1995).
"Neutron Reflectometry with Polarization Analysis: A Theory and a New Spectrometer."
Hercules Courses, Neutron and Synchrotron Radiation for Condensed Matter Studies (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1993).
D. A. Korneev, V.I. Bodnarchuk and V.K. Ignatovich, JETP Lett. 63, pp. 944-951 (1996).
"Off-Specular Neutron Reflection From Magnetic Media with Nondiagonal Reflectivity Matrices."
Majkrzak C.F. and Berk N.F., Physical Review B 52 (15), pp. 10827-10830 ( 1995).
"Exact Determination of the Phase in Neutron Reflectometry."
F. Ott and C. Fermon, Physica B 234-236, pp. 522-524 (1997).
"Spin Analysis and New Effects in Reflectivity Measurements."
R. Pynn, Phys. Rev. B 45, pp. 602-612 (1992).
"Neutron Scattering by Rough Surfaces at Grazing Incidence."
V. F. Sears, Neutron News 3 (3) (1992).
"Neutron Scattering Lengths and Cross Sections."
S.K. Sinha, E.B. Sirota, S. GAroff and H.B. Stanley, Physical Review B 38 (4 ), pp. 2297-2311 (1988).
"X-Ray and Neutron Scattering from Rough Surfaces."
S.K. Sinha, Physica B 174, pp. 499-505 (1991).
"Complementary of Neutrons and X-Rays as Probes of Surfaces and Interfaces."
Y. Yoneda, Physical Review 131, pp. 2010-2013 (1963).
"Anomalous Surface Reflection of X-Rays."
H. Zabel, Physica B 198, pp. 156-162 (1994).
"Spin Polarized Neutron Reflectivity of Magnetic Films and Superlattices"
Grégory
Chaboussant ( Tel : 01 69 08 96 51, chabouss@dsm-mail.saclay.cea.fr)
Sébastien Gautrot ( Tel : +33 1 69 08 86 26, gautrot@dsm-mail.saclay.cea.fr)
Fax: +33 1 69 08 82 61
Sébastien Gautrot ( Tel : +33 1 69 08 86 26, gautrot@dsm-mail.saclay.cea.fr)
Fax: +33 1 69 08 82 61
LABORATOIRE LEON BRILLOUIN (CEA/CNRS)