Sources de lumière extrême et métrologie optique / Extreme light sources and optical metrology
Sources de lumière extrême et métrologie optique / Extreme light sources and optical metrology
Plusieurs équipes du LIDYL contribuent au développement de sources de lumière extrême (impulsions lasers ultra intense / ultra brèves), ainsi qu'au nécessaire développement de la métrologie optique associée avec la mesure de profil d'intensité ultra-intense ou de durée d'impulsions dans le domaine attoseconde (10-18 s).
 Instrumentation et soutien à la recherche (LIDYL/SLIC)
Instrumentation et soutien à la recherche (LIDYL/SLIC)
L'équipe SLIC (Supports et Lasers à Impulsions Courtes) du LIDYL est un groupe de développement laser et de support technique. La mission principale de SLIC est de fournir des lasers de pointe pour les utilisateurs internes (LIDYL) et externes (nationaux et internationaux).
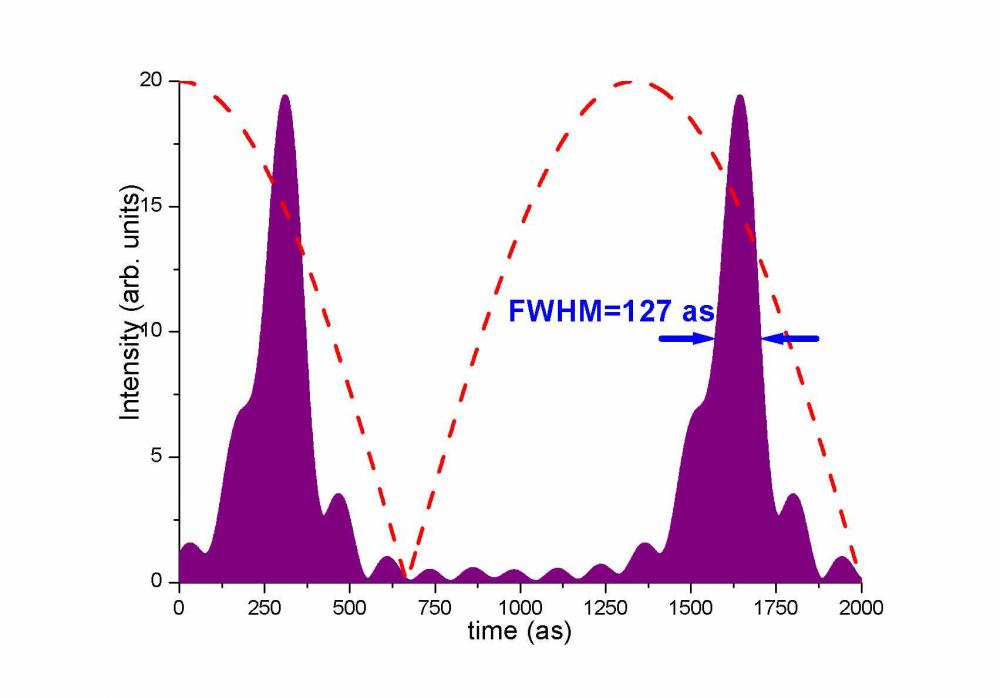
 Physique et chimie femtoseconde-attoseconde / Femtosecond-attosecond physics and chemistry
Physique et chimie femtoseconde-attoseconde / Femtosecond-attosecond physics and chemistry
While the pulse durations of infrared lasers are reaching the fundamental limitation imposed by the duration of the optical cycle (a few femtoseconds), High-order Harmonic Generation has recently opened a new field by accessing the attosecond regime (1as = 10-18 s). HHG spectra are made of lines corresponding to the odd multiples of the fundamental laser frequency, and can cover a very broad spectral range, from visible light to soft X-rays.

 Simulation numérique et calcul haute performance
Simulation numérique et calcul haute performance
Au LIDYL, les simulations numériques permettent de modéliser l'interaction de la lumière avec la matière en particulier sous l'effet d'impulsions laser de très haute intensité et extrêmement brèves (domaine attoseconde (10-18 s).
 Spectroscopies laser pour les applications / Laser spectroscopy for applications
Spectroscopies laser pour les applications / Laser spectroscopy for applications
La matière sous toutes ses formes est quantifiée. Atomes, molécules des molécules simples aux macromolécules biologiques, présentent des spectres lumineux caractéristiques, en absorption ou en émission, que l'on peut identifier par spectroscopie. Les sources lasers et plus particulièrement les sources impulsionnelles permettent aujourd'hui de nouveaux développements de tous les types de spectroscopies.
 Biologie et santé / Biology and health @ NIMBE
Biologie et santé / Biology and health @ NIMBE
Plusieurs laboratoires du NIMBE ont une activité de recherche en lien avec la biologie ou la santé : Le LICSEN développe des technologies innovantes permettant d'obtenir des surfaces et nanostructures fonctionnalisées qui ont de multiples applications pour la biologie et les soins de santé : biocapteurs, implants, administration de médicaments, surfaces bactéricides...
Les recherches fondamentales sur les matériaux permettent de développer des méthodes pour élaborer des matériaux complètement nouveaux aux propriétés originales. Ces recherches permettent d'adapter les matériaux pour obtenir les meilleures performances dans la réaliation de dispositifs électroniques ou optiques.
 Nouvelles technologies de l'énergie @ NIMBE
Nouvelles technologies de l'énergie @ NIMBE
Un effort intense de recherche fondamentale est indispensable aujourd'hui, pour pouvoir proposer demain de nouvelles avancées technologiques originales, permettant de faire faire face à la transition énergétique, permettant la nécessaire réduction de nos émissions de CO2.
Caractérisation de matériaux pour l'énergie / Characterization of materials for energy
Les différentes filières énergétiques, telles que l'énergie nucléaire ou encore les nouvelles technologies autour de l'hydrogène, vecteur énergétique, ou le photovoltaïque, demandent des matériaux adaptés, dont il faut tester la durabilité et la fiabilité.
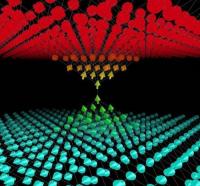
Electronic structure and atomistic modelisation
Several IRAMIS teams are involved in calculations of the electronic structure (ab-initio , tight binding, Hückel methods, etc...) and more generally in the modeling of matter at the atomic scale, which also includes more phenomenological methods (empirical potentials, model Hamiltonians, etc...) These modeling tools are mainly developed and used in physics (spectroscopy, transport, magnetism), chemistry (reactivity, dynamics) and for the study of materials (diffusion, growth, defects).
Environmental chemistry and pollution control (Earth science)
This topic shared between the CEA, the CNRS, the 'Institut de Physique du Globe' of Paris and the University Pierre and Marie Curie (Paris VI) called upon environment and Earth sciences with physics and chemistry. Developed research combines tests at the laboratory, ground studies and powerful analysis tools like the neutron activation or the nuclear microprobe. This research relates to mainly magmatology and volcanology which implement two approaches of chemical geodynamics.

Etudes métallurgiques par diffusion de neutrons / Metallurgical studies by neutron scattering
Les neutrons constituent une sonde particulièrement intéressante pour étudier la structure des matériaux : ceci en particulier grâce à leur faible absorption permettant de travailler sur des pièces d'épaisseur centimétrique, et aussi grâce à la relative facilité de réaliser des expériences en conditions complexes (températures élevées, matériau sous contraintes, ...).
From molecules to molecular materials
To get objects with original features, making molecular materials is addressed by assembling building blocks, as atoms, simple or complex molecules or nanostructures (carbon nanotubes, and graphene sheets in particular) on metallic, inorganic or organic supports, glass ... by "bottom-up" processes.
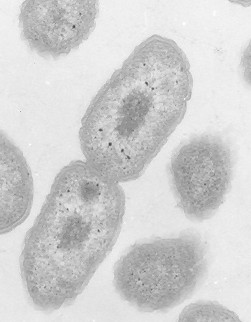
Human and Environmental Toxicology
Today, industrial and scientific activities employing radioactive elements produce considerable amounts of waste that may pose a risk to the environment and to public health due to their chemical and ionizing properties. Understanding the transfer mechanisms of such anthropogenically derived elements in the environment and their possible accumulation in living organisms is necessary for the assessment of their environmental toxicity.
Interfaces, complex fluids and microfluidics
Depending on the field (low-carbon energies, nanoscience for information and health technologies (fundamental research for IT and HIT), radiation-matter interaction), several IRAMIS teams are involved in this topic.

IRAMIS and the European Large Instruments
From their activities of Basic Research, the scientists of IRAMSI are very present around the French and foreign Large Research Instruments: le Laboratoire Léon Brillouin (LLB), within IRAMIS, and also: l'Institut Laüe-Langevin, the synchrotron facilities (ESRF, ELETTRA et SOLEIL,....), the GANIL ...
Research on this topic focuses on fundamental studies of the behavior under irradiation of a wide variety of materials used in the context of nuclear power (metal alloys, glass, ceramics, polymers). The experiments involve external irradiation tools (ion accelerators or electrons), and at the same time benefit from important simulation efforts.

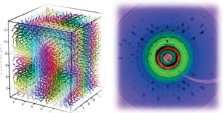
Materials and nanosciences, fundamental studies and applications
This scientific axis covers the activities related to the research in materials science and more generally in hetero-systems (i.e., interfaces, alloys, composites materials, and confined systems). The topics cover the study of the detailed st ructure of nanoobjects, the interactions between nano-objects, and the role of nanost ructures in composite materials. The techniques used for these studies range from diffraction to small angle scattering and reflectivity.
Matière excités et défauts au CIMAP
Sur ce thème, les objectifs de recherche portent sur la compréhension des processus actifs dans la matière lors des excitations électroniques et sur les défauts structuraux.
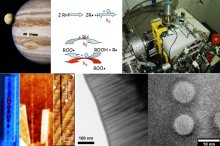
Matter under Extreme Conditions
The MEC laboratory is a fundamental research lab where two closely related topics are investigated, on the one hand the interaction of matter with a strong laser field, i.e., at high power density, on the other hand the matter at very high energy density, i.e., hot dense plasmas. The MEC lab is composed of 3 interacting research groups, namely Attophysics, Physics at High Intensity (PHI), and High Energy Density Matter (HEDM).
Molecular assembly and nanostructured materials
In many liquid or solid materials of our everyday life matter appears as highly divided. The precise organization of the finely divided components from the microscopic to the macroscopic scale has a huge implication on the properties of these materials. Many of these nanostructured materials are classified as "soft matter".
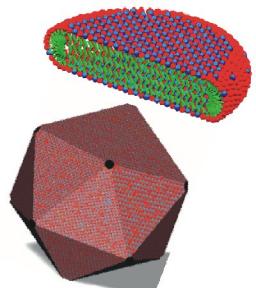

The development of nanotechnology based nowdays on the assembly (or even self-assembly) of building blocks that are nanoparticles. The goal is to make use of the intrinsic properties of nanoparticles such as their plasmonic capacities, high surface area or reactivity and of their assembly, to obtain new functional devices such as nanofiltration membranes or photonic crystals.
Nanomagnetism, spintronic and multiferroic materials
This research topic focuses on the development and study of: magnetic materials or multiferroic oxides (ferroelectricity associated with magnetism)* the magnetization dynamics in hybrid nanostructures and its coupling to the spin currents (spintronics) development of ultra-sensitive magnetic sensor and the associated modeling.

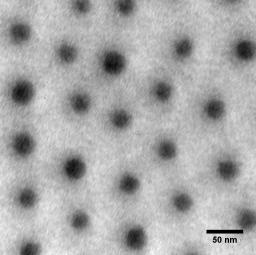
Nanostructured materials and nanocomposites
In very many situations, whether it be in fluids or materials for every day use, or in biological systems, matter is present in a highly dispersed form. It follows an extraordinary range of behaviour due to structural combinations, from the molecular to the mesoscopic and macroscopic scale.
Du fait de leur taille, les nanoparticules peuvent interagir avec les éléments du vivant, de la cellule à la molécule biologique. Ceci peut être mis à profit en médecine pour cibler des traitements, mais peut aussi présenter des effets indésirables, lors d'une forte exposition.
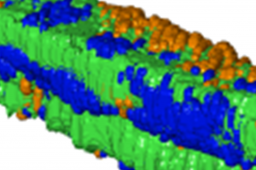
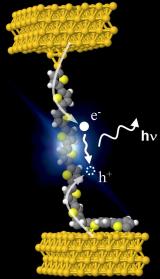
Organic and molecular electronics
With organic and molecular electronics, a data processing based on various types of nano-objects (molecules, biomolecules, nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, graphene,...) is emerging.
Three research programs of the IRAMIS found an natural extension towards biology: Molecular engineering, where studies of co-operative interactions of molecules in solution found a direct extension towards studies of proteins and of the various assembly modes of biological interest molecules, Matter with high density of energy, where radiolysis, molecule radiation interactions, can be directly transposed to molecules like the ADN, Divided ultra matter, where nanostructured materials, nanophysics and biology converge.
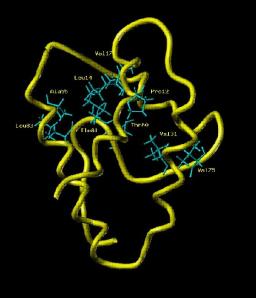
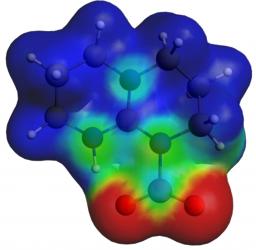
Quantum chemistry and molecular simulations
Theoretical chemistry studies (quantum chemistry, classical and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations) at LCCEF focus on lanthanides and actinides compounds. Domains of application are medical imaging (e.g., MRI) and nuclear sciences. The goal of these theoretical studies is to design new molecular frameworks in liquid state. Some methodological developments are also conducted.
Recherche et développement laser (@ LIDYL/SLIC)
Le groupe SLIC mène des programmes de R&D visant à maintenir les plates-formes laser du LIDYL à un haut niveau de performances et à les adapter aux nouveaux besoins de leurs utilisateurs.

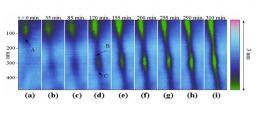
Statistical physics in mechanics
Understanding the relations between materials microstructure and their mechanical properties is of outmost importance in geophysics and for industrial design. Concerning material failure, the competition between stress enhancement in the vicinity of cracks and disorder in the material microstructure makes it rather complex to predict. However, the tools of out-of-equilibrium statistical physics provide the proper framework to describe crack growth.
Strongly correlated quantum materials and magnetism
This scientific axis encompasses research activities on a large variety of magnetic and/or strongly correlated electron systems. Included are studies of unconventional superconductors (cuprates, pnictides), geometrically frustrated pyrochlore magnets (spin ices), novel magnetic orders in 4f-electron systems (heavy fermions, Kondo insulators), multiferroic compounds with interplay between electric and magnetic orders, manganites with giant magnetoresistance properties, and molecular magnets.
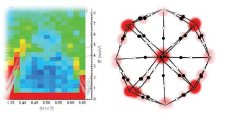
Supramolecular, structural and coordination chemistry
In this domain, the field of study of DRECAM covers the molecule to the controlled assembly of molecules. This approach extends from the fine comprehension of molecule - metal coordination and interaction, to the construction and the synthesis of molecular assemblies having specific properties (structure, complexation, solubility, biological activity) and finally to their characterization by specific tools such as solid or liquid NMR, X-ray or neutron scattering and near field microscopies.

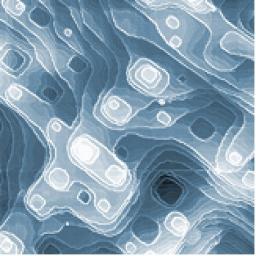
The outstanding properties of nanostructures (morphology, magnetism, catalytic ...) are today more and more exploited. These nanostructures are usually obtained on a substrate where interatomic forces induce the spontaneous organization of matter at the nanometer scale. Studying the structures of surfaces and their dynamical properties (at equilibrium, fluctuations, growth, evaporation …) allows pointing out the basic laws for the matter organization at this scale.
La plupart des synthèses chimiques sont réalisées en milieu liquide. Pour l'élaboration de nanoparticules et les nanomatériaux, de multiples méthodes de synthèse en phase gaz se révèlent particulièremetn utiles et performantes .

Systèmes désordonnés et matériaux / Disordered systems, materials
Liquides élémentaires Liquides complexes (ionique et olymèriques) Liquides conditionnés (sous haute pression, confiné, solutions) Verres d'oxyde et chalcogenures Cristallisation Transition vitreuse Simple liquids Complex liquids (ionic and polymeric) Liquids in special conditions (high pressure, confined, in solutions) Oxyde glasses and chalcogenures Crystallization Glass transition
Thématiques NFMQ : magnétisme, transitions de phase - Etudes par diffusion de neutrons
Le magnétisme est un domaine d’intérêt majeur, car combiné à l’électronique, il a modifié en profondeur notre vie quotidienne : sous forme de capteurs, d’actionneurs, de dispositifs nomades (téléphones, tablettes, ordinateurs portables), de matériaux aux capacités de stockage accrues pour l'enregistrement magnétique de toutes nos données informatiques., etc...
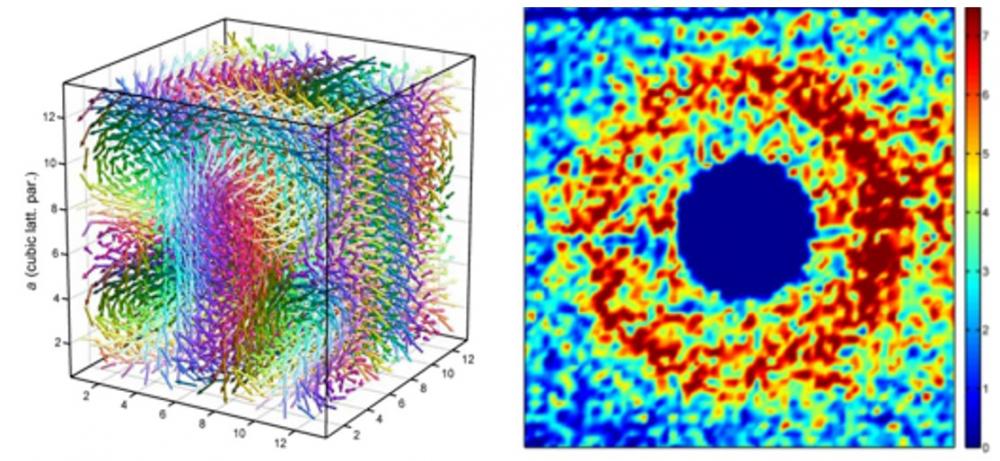
Transformations catalytiques pour l’énergie
L’IRAMIS développe de nouveaux catalyseurs avec l'objectif de développer le stockage des énergies alternatives sous forme chimique, ou la conversion du CO2, la transformation de la biomasse, et le recyclage des déchets polymériques, trois sources de molécules de base pour l’industrie chimique, aujourd’hui issues de produits pétroliers.
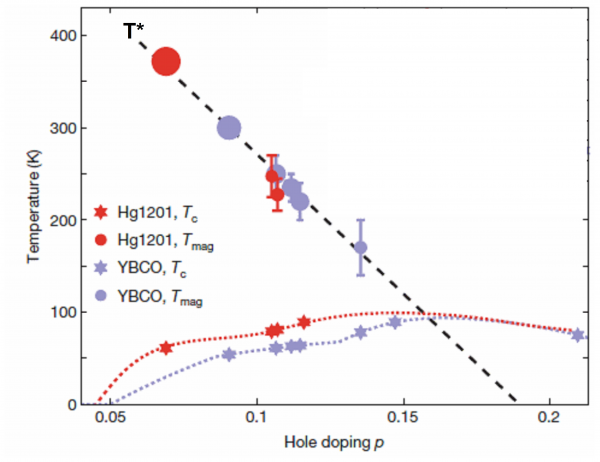
Unconventional superconductivity: neutron spectroscopy and theory
In the last two decades, new superconducting (SC) compounds, exhibiting surprisingly high critical temperatures (Tc), have been discovered. In contrast to conventional superconductors, the SC order parameter is not isotropic, neither in cuprates nor in Fe-based systems. This ignited a search for new SC pairing mechanisms based on the existence of rather strong electronic interactions.

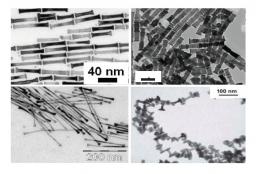
Nano-chimie, nano-objets / Nano-chemistry, nano-objects
Le développement des nanotechnologies s'appuie de plus en plus sur la logique d'assemblage spontané (auto-assemblage) ou non, des briques élémentaires que sont les nanoparticules.
 Économie circulaire - environnement @ NIMBE
Économie circulaire - environnement @ NIMBE
Plusieurs thématiques de recherche du NIMBE concourent à mieux contrôler notre environnement (analyse, méthodes) et assurer la meilleure gestion possible de nos déchets : Recyclage (LICSEN) La maitrise de nos ressources en éléments chimiques de haute valeur, la nécessité de ne plus rejeter de carbone fossile dans l'atmosphère imposent aujourd'hui une transition énergétique et économique majeure, où le recyclage de nos matières premières (terres rares, plastiques, CO2.

De nombreuses méthodes sont développées par les équipes du NIMBE (LEDNA, LICSEN, LIONS, LSDRM) pour développer des capteurs chimiques ou biochimiques sensibles, sélectifs et efficaces.
Chimie environnementale et dépollution / Environmental chemistry and depollution
Les nanotechnologies offrent de nombreuses méthodes innovantes pour le piégeage de nombreux éléments polluants, chimiques, biologiques ou encore des métaux lourds. Des méthodes de dépollution à l'aide de filtres à base de matériaux nanoporeux ou de fibres de carbone fonctionnalisées sont ainsi développées au LICSEN.


Statistical physics and complex systems
The understanding and control of the structure, texture, composition, kinetics of evolution of materials and thus of their physical chemical or mechanical properties are a major stake in wide fields. In much cases, the materials which one wishes to use for a given application are intrinsically evolutionary. Out of equilibrium dynamics may affect the mechanic, magnetic or electric properties of a number of materials.
The development of new technologies for energy implies mastering the process of conversion between the different forms (solar, thermal, chemical, electrical, mechanical, etc.), as well as storage processes: Solar energy can be directly transformed into electrical energy via the photovoltaic process and stored in accumulators. It can also be transformed directly into chemical energy (hydrogen) by photocatalysis.
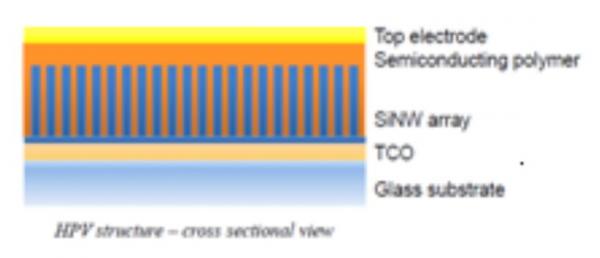

Photosciences: Light plays a role in many physical and chemical processes; it is also an exceptional tool in the investigation of matter. Photo-scientists within laboratories of IRAMIS study the interaction between light and matter as a fundamental process and an analysis tool. Lasers: Photoscience is becoming increasingly important due to the rise of ultra-short light pulses, often ultra-intense.
Solids, surfaces interfaces and materials
Solids, surfaces, interfaces and materials: The ability to understand and foresee properties and functionalities for future materials relies on the comprehension of various fields of science and technical skills, ranging from the most fundamental to potential applications.

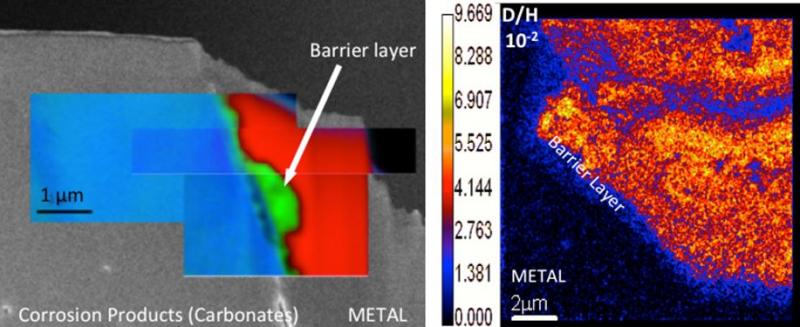
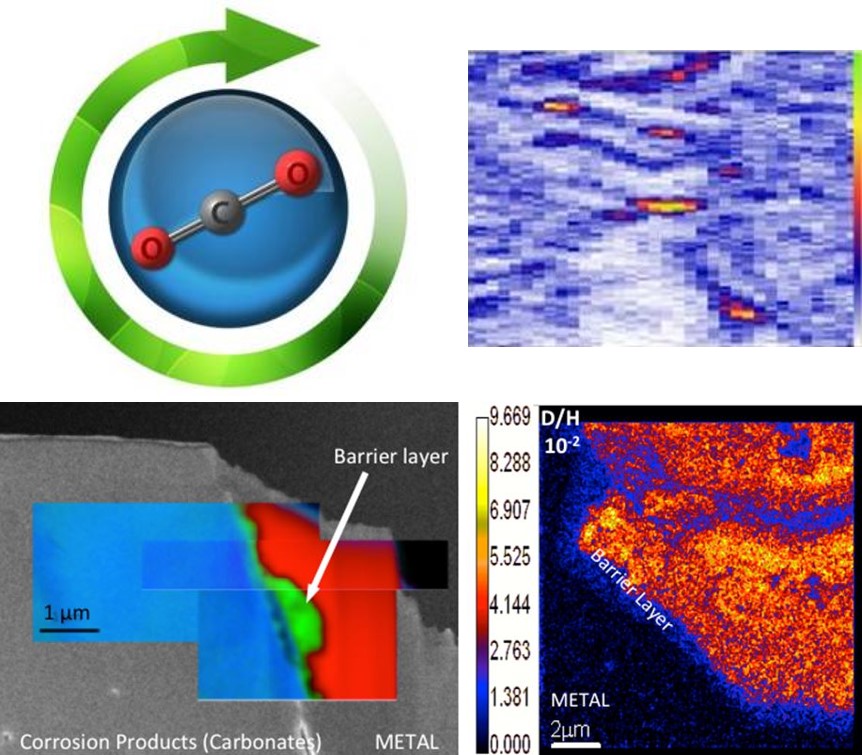
Plusieurs pays envisagent de développer une technologie de barrières multiples pour la sécurité du stockage des déchets nucléaires. Une question centrale est de savoir modéliser le comportement sur le long terme (soit 100 à 1000 ans) des matériaux utilisés, en particulier des containers, en acier faiblement allié, et de la matrice vitrifiée.
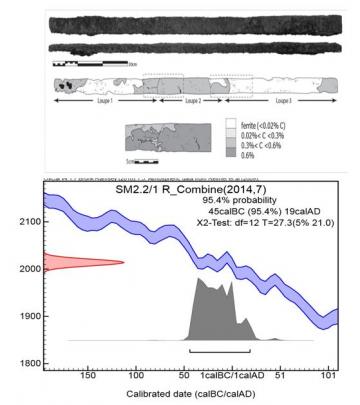
Au delà des études visant à mieux comprendre et prédire l'altération des métaux anciens, l'équipe du LAPA utilise la science des matériaux et les méthodes de la chimie pour comprendre certains aspects des sociétés antiques en lien avec leur niveau technologique.
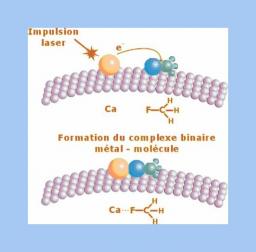
Physico-chemistry and Chemical-physics
A chemical reaction depends not only of atoms and molecules involved but also of their short range environment. Understanding a chemical reaction demands a fundamental approach taking into account both temporal and spatial features. Therefore, IRAMIS implements with lasers, time-resolved spectroscopies in the range from femtosecond to the millisecond, to study the dynamics of molecular systems, like for example DNA biomolecules, or chromophore molecules for photovoltaics.