2013
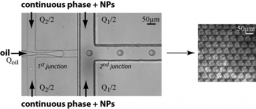
Emulsions of two immiscible fluids stabilized with solids particles, called Pickering emulsion, have been studied since the early twentieth century and the pioneering works of Ramsden[1] and Pickering[2] The irreversible adsorption of particles at the interface of the two phases gives original properties of these emulsions. Such emulsions are of primary interest in the food, cosmetics industry and oil recovery. Although it is now clear that the stabilization mechanism comes from the partial wettability of the nanoparticles by the two emulsion phases, the interface structures for such a stability mechanism is not well understood. There is a need of making a Pickering emulsion model system where the nanoparticles are well controlled as well as the emulsion size. The LIONS laboratory has developed a microfluidics platform (Fig.6) which allows preparing monodisperse tunable Pickering emulsion starting from monodisperse silica nanoparticles (NPs) of 7nm radius.