 Long-period helical structures and twist-grain boundary phases induced by chemical substitution in the Mn1−x(Co,Rh)xGe chiral magnet.
Long-period helical structures and twist-grain boundary phases induced by chemical substitution in the Mn1−x(Co,Rh)xGe chiral magnet.
 Long-period helical structures and twist-grain boundary phases induced by chemical substitution in the Mn1−x(Co,Rh)xGe chiral magnet
Long-period helical structures and twist-grain boundary phases induced by chemical substitution in the Mn1−x(Co,Rh)xGe chiral magnet
N. Martin, M. Deutsch, G. Chaboussant, F. Damay, P. Bonville, L. N. Fomicheva, A. V. Tsvyashchenko, U. K. Rössler and I. Mirebeau
Phys. Rev. B 96, 020413(R) – Published 21 July 2017.
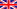
We study the evolution of helical magnetism in MnGe chiral magnet upon partial substitution of Mn for 3d-Co and 4d-Rh ions. At high doping levels, we observe spin helices with very long periods—more than ten times larger than in the pure compound—and sizable ordered moments. This behavior calls for a change in the energy balance of interactions leading to the stabilization of the observed magnetic structures. Strikingly, neutron scattering unambiguously shows a double periodicity in the observed spectra at x = 0.5 and >0.2 for Co- and Rh-doping, respectively. In analogy with observations made in smectic liquid crystals, we suggest that it may reveal the presence of magnetic “twist grain boundary” phases, involving a dense short-range correlated network of magnetic screw dislocations. The dislocation cores are here tentatively described as smooth textures, made of nonradial double-core skyrmions.