Pages scientifiques 2008
General objectives
We aim at understanding the microscopic mechanisms controlling the formation of nanoparticles. Different types of NPs are studied in the LIONS and among them gold NPs have already been the subject of several achieved PhD (B. Abécassis and F. Hubert) and on-going in-house studies (J. Han) and collaborative ones (S. Gomez from the Univiersity og Vigo). Our general approach is to consider that quantitative kinetic measurements of the size, size distribution and number of NPs with time together with the gold atoms speciation in solution (Au(III), Au(I) and Au-0)) can serve as a basis to develop a better understanding of the mechanisms involved.
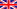
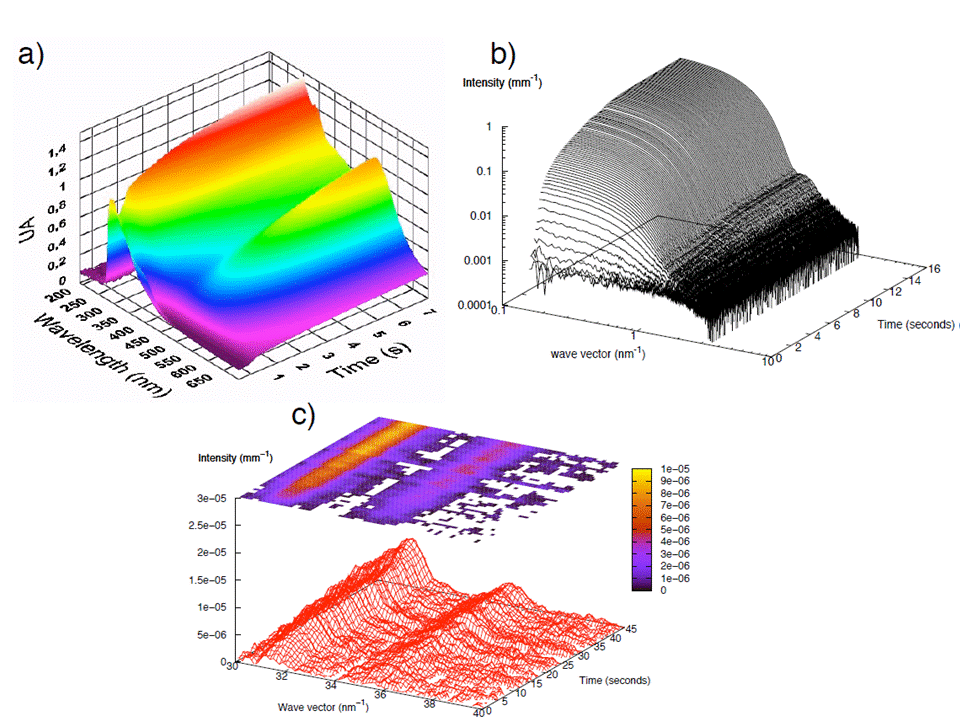
The nucleation and growth mechanism of gold nanoparticles are followed at the millisecond time scale using different in situ techniques. Three different systems are presently studied : nanospheres in toluene (NST), nanorods in water (GNR) and nanospheres in water (NSW). The time scale range from one second (NSW) to 600 seconds (GNR). The sample environment are adapted to the time-scale involved. They are (i) a stopped for the most rapid synthesis, (ii) an home-made millifuidic set-up for water rapid systems and (iii) a simple flow through cell for the GNRs.
Three main synchrotron based techniques are used, SAXS WAXS and XANES both with a high time resolution. ESRF (ID02) and SOLEIL (SWING and ODE) have been intensively used to acquire a unique set of data during the nucleation and growth of these objects.