Jan 30, 2011
In collaboration with chemists of ENS Lyon and biophysicists of DSV (IBiTeC-S), a team of LSDRM (IRAMIS/SIS2M) designed a cellular probe taking advantage of the extreme sensitivity of NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) of hyperpolarized xenon*. The experiment shows the excellent selectivity of the method to detect the chosen molecular target .
Feb 15, 2010
Chemists of DSV (CEA-Life science Division) and physicists of DSM (CEA-Matter science Division) specialists of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) have developed a new solid state NMR apporach to measure long inter-atomic distances. Based on the use of tritium, the hydrogen isotope with the highest sensitivity to NMR, this technique allows the determination of the conformation of small molecules bounded to their biological receptors.
Jan 13, 2010
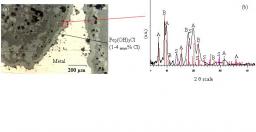
P. Maillet*, C. Levard**, E. Larquet§, C. Mariet,* O. Spalla*, N. Menguy§, A. Masion**, E. Doelsch‡, J. Rose** et Antoine Thill*
Imogolites (OH)3Al2O3Si(OH) are natural minerals discovered in 1962 in Japanese volcanic soils. Their structure is similar to that of a carbon nanotube. They are made of a curved Gibbsite sheet Al(OH)3 forming a nanotube of 2 nm in diameter. The tetrahedral silicon adsorbed inside the nanotube controls its curvature. The diificulties to synthesized large quantities of this mineral have indered the development of industrial applications.
Sep 22, 2009
D. Kopetzki, Y. Michina, T. Gustavsson, D. Carrière
Amphiphilic molecules have a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic chain. Under certain conditions, they can self-organize into hollow spherical hollow vesicles with a surfactant bilayer enclosing an aqueous core, the overall diameter ranging from a few tens of nanometers to several microns. By carefully choosing specific preparation conditions, the scientists of SIS2M have shown that extremely robust aggregates can be synthesized with an interesting potential for encapsulation.
Mar 31, 2009
H. Desvaux, D. J.Y. Marion, G. Huber, P. Berthault
In nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) whose medical application is known as MRI, it is the voltage at the extremities of a coil that is usually monitored, since it reflects the variation of the induction created by the precession of the nuclear magnetization after a radiofrequency (RF) excitation pulse. The nuclear magnetization results from the difference in population between the spin states, induced by the strong static magnetic field.
Jan 15, 2009
J.-P Dognon, C Clavaguéra, and P. Pyykko
J.-P Dognon : CEA Saclay - IRAMIS/SCM (France) C Clavaguéra : Laboratoire des Mécanismes Reactionnels, Ecole Polytechnique, CNRS, 91128 Palaiseau (France) P. Pyykko : Department of Chemistry, University of Helsinki, Finland
Jun 08, 2007
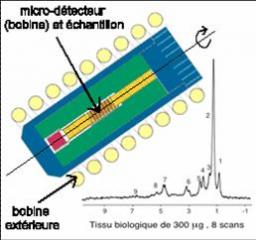
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is an indispensable technique for studying matter. It can be applied to medical imaging (MRI) to obtain 2D and 3D images of the human body. While it opens the door to a wealth of physicochemical information by harnessing the fundamental properties of matter, NMR remains a technique with poor sensitivity, making it very difficult to use on small quantities of solid or heterogeneous material.
Apr 13, 2007
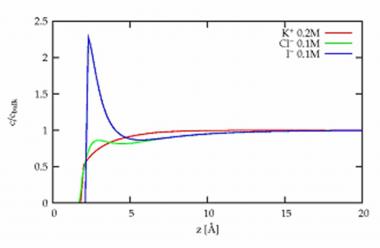
P. Viswanath, J. Daillant, L. Belloni, M. Alba, DRECAM/SCM – Service de Chimie Moléculaire, S. Mora (LCVN, Montpellier) et O. Konovalov (ESRF).
When a salt like NaCl is dissolved in water, sodium and chlorine separate in ionic form Na+ and Cl-, become surrounded by water molecules and disperse. This deeply modifies the nature of the solvent which becomes for example, a good electricity conductor. At the surface, the distribution of the ions remains however poorly known, although many "contact" properties depend on it.
Mar 25, 2005
D. Neff, P. Dillmann, L. Bellot-Gurlet*, G. Béranger**
One of the most important technological challenge of the century is the safe storage of nuclear wastes. In France, one part of the engineered barrier designed to separate the biosphere from wastes is a low alloy steel overpack. Thus, it is necessary to predict the very long term corrosion behaviour of this overpack for several centuries.