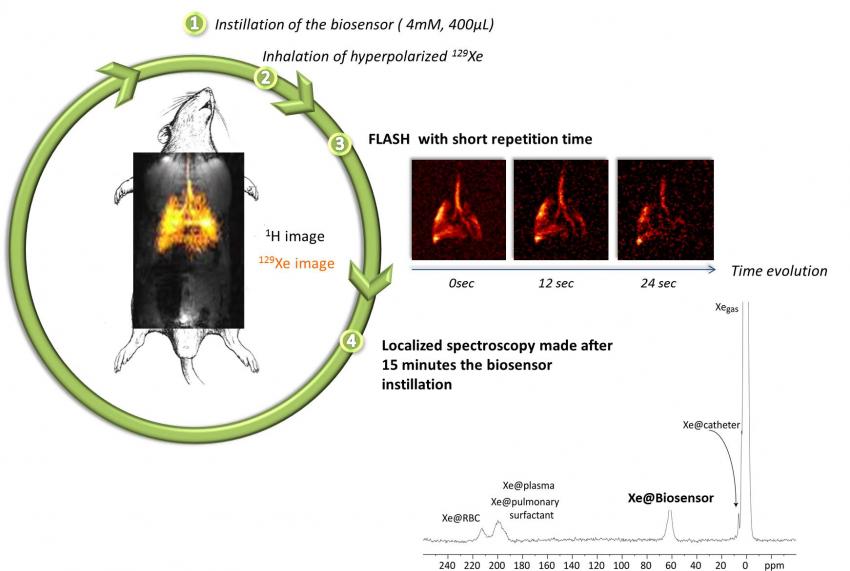
IRAMIS "Saclay Institute of Matter and Radiation" is the 2nd Institute in size of the CEA Fundamental research Division (DRF). IRAMIS gathers 6 joint Research Units in association with CNRS, Ecole Polytechnique or ENSICAEN. Four are located on the CEA Research Centre of Saclay (LIDyL, LLB, NIMBE and SPEC), one on the site of the Ecole Polytechnique (LSI) and one in Caen (CIMAP), close to GANIL.
Discover the IRAMIS: - by Research Programs - by Units - by Techniques
Mostly fundamental, the research in physics and chemistry carried out at the Institute are in close connection with societal issues and CEA programs :
- Nanoscience for communication and health technologies
- Radiation-matter interactions
- Low carbon energies
To carry out this research program, the teams of IRAMIS implements leading foreground facilities and scientific equipments, and are also very active around the Great Europeans Instruments.
Mostly fundamental , research carried out at the Institute are open to the creation of economic value and technology transfer. IRAMIS also contributes to 4 EQUIPEX and 4 LABEX of the "Investments for the Future" programmes of the French government.