Feb 02, 2024
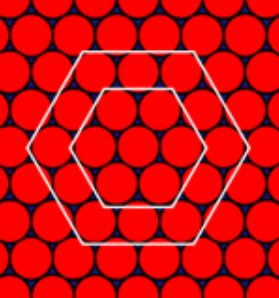
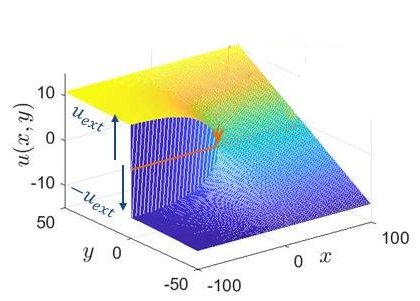
Active particles can form two-dimensional crystals that are different from those formed by passive particles in equilibrium, showing extreme spontaneous deformation at large scales without melting.
Nov 16, 2021
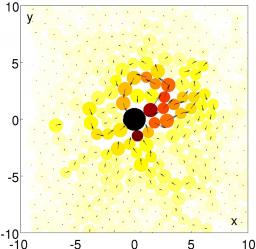
In a recent paper published in PNAS, Hugues Chaté (IRAMIS/SPEC), Xia-qing Shi and the group of Tian Hui Zhang (Soochow University) show that subcritical active matter exhibits novel collective self-organized dynamics. They used “Quincke rollers”, i.e. colloidal spheres at the bottom of a cell filled with conducting fluid submitted to a vertical electric field.
Feb 19, 2021
Une équipe réunissant des chercheurs du SPEC, de l’IPhT et de l’ENS-Paris a montré l’absence de transition de Gardner dans un verre moléculaire archétypique – le glycerol - jusqu’à une température de 10 K.
Jul 08, 2020
Contacts SPEC : Dana Stanescu, Helene Magnan, Jean-Baptiste Moussy, Cindy Rountree, Antoine Barbier
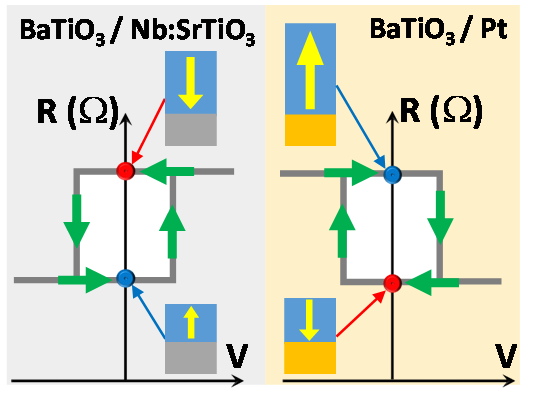
Les matériaux ferroélectriques ont connu un essor considérable en raison de leurs applications potentielles dans des domaines comme la spintronique ou la conversion de l’énergie solaire1–3. Au SPEC nous avons étudié le rôle des interfaces, du substrat et des couches d’oxyde supérieures sur les propriétés ferroélectriques des hétérostructures à base des couches minces de BaTiO34.
Dec 13, 2019
La ténacité d’un matériau définit sa résistance à rupture. Si on sait la mesurer expérimentalement de manière précise, on ne sait pas, à l’heure actuelle, prévoir sa valeur à partir de la structure atomistique du matériau considéré, même dans les cas les plus simples.
Jan 23, 2017
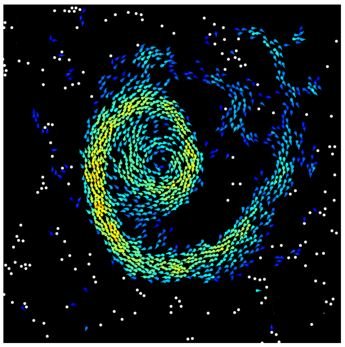
An international team published in Nature, the discovery and interpretation of a surprising form of biological collective motion: They observed that millions of motile cells in dense bacterial suspensions can self-organize into highly robust collective oscillatory motion, while individuals move in an erratic manner.
Jan 23, 2017
A team of the Condensed State Physics Unit (IRAMIS/SPEC – UMR 3680 CEA-CNRS) is coordinator of the 4 years (2017-2020) European project H2020 - FET Proactive * MAGENTA, which is launched on January 23, 2017. This € 5 million funded project brings together 10 European partners to open a new technological path in the search for magneto-thermoelectric materials and devices, optimized for residual heat recovery applications.
Jun 01, 2016
Les verres forment l’essentiel de nos matériaux du quotidien, et prennent une place croissante dans les technologies modernes (fibres optiques, etc…).
Nov 23, 2011
K. Katsuyoshi, D. L'Hôte, S. Nakamae, M. Konczykowski, V. Mosser
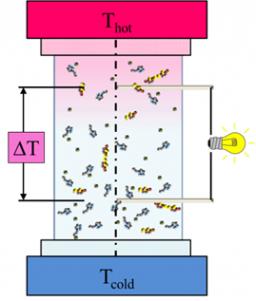
Le théorème de fluctuation-dissipation, reliant l'intensité des fluctuations d'une observable à la réponse à une sollicitation, est un principe vérifié pour tous les systèmes à l'équilibre thermodynamique.
Jul 18, 2011
( Version française)
Stress corrosion - combined action of mechanical stress and corrosion by water from the surrounding atmosphere - is often the cause of crack propagation in glasses. A study by neutron reflectivity at the Laboratoire Léon Brillouin (IRAMIS / LLB) of samples of silica glass fractured under an atmosphere of heavy water (D2O) shows a high penetration of water into the glass.
Mar 30, 2010
( Version française)
Researchers in the Instability and Turbulence Group of IRAMIS-SPEC have succeeded in experimentally characterizing the non linear mechanical response of an amorphous granular media across the jamming transition. They have demonstrated that global rigidity sets in via the critical growth of a correlation length.
Jul 15, 2008
D. Bonamy and L. Ponson (SPCSI), D. Santucci (Fysik Institutt Oslo)
Fracture is a phenomenon of everyday life: it is observable at all scales of condensed matter, from the atomic scale (in nanostructures) to the scale of our planet marked by fractures in the continental plates. But, can we find a unifying model to describe the phenomenon?
The dynamics of fracture is complex.
Sep 25, 2007
Le mélange des fluides très visqueux intervient dans de nombreux procédés industriels, mais est également présent dans la vie courante. Pour mélanger une pâte à gâteau, par exemple, un enfant va intuitivement remuer les ingrédients avec une cuillère.
Mar 29, 2007
VKS collaboration (CEA-CNRS-ENS Lyon and Paris), CEA contact: Francois Daviaud
Over the geological ages, the Earth has undergone several erratic reversals of its magnetic field. The sun’s magnetic field is reversed regularly every 22 years according to its cycle. These magnetic dynamics, which are still shrouded in mystery, play a role in our planet’s exposure to cosmic rays.
Mar 28, 2007
M.-A. Dubois1, L. H. Emmons2, L. Cournac3, P. Chatelet4, N. C. A. Pitman5, V. Vilca5, & L.-F. del Aguila6
1CEA Saclay, DSM/DRECAM/Service de Physique de l ’Etat Condensé, L ’Orme des Merisiers, 91191 Gif sur Yvette, France
2Department of Zoology NHB 390 MRC 108, Smithsonian Institution, P.O.
Jan 27, 2007
A. Chiffaudel, F. Daviaud, B. Dubrulle, C. Gasquet, R. Monchaux, V. Padilla, avec la participation de L. Marié et F. Ravelet, DSM/DRECAM/SPEC
Collaboration VKS : CEA – ENS Lyon – ENS Paris -
Collaboration VKS : CEA – ENS Lyon – ENS Paris -
Many research teams aim at understanding of the origin and behavior of the magnetic field of planets and stars. The VKS1 collaboration (gathering researchers at CEA, CNRS, Ecoles normales supérieures in Lyon and Paris) has succeeded in generating a magnetic field from a highly turbulent liquid sodium flow in a laboratory experiment.