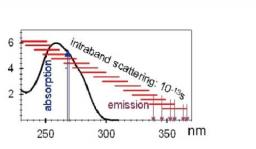
Absorption of UV radiation by DNA bases is known to induce carcinogenic mutations. The lesion distribution depends on the sequence around the hotspots suggesting cooperativity between bases. Here we show that such cooperativity may intervene at the very first step of a cascade of events by formation of Franck-Condon states delocalized over several bases and subsequent energy transfer faster than 100 fs. Our study focuses on the double helix poly(dA).poly(dT), whose fluorescence, induced by femtosecond pulses at 267 nm, is probed by fluorescence upconversion and time-correlated single photon counting, over a large time domain (100 fs – 100 ns). The time-resolved fluorescence decays and fluorescence decays are discussed in relation with the steady-state absorption and fluorescence spectra in the frame of exciton theory.
•  Physique et chimie pour le vivant et l’environnement › Physique et vivant / Physics and life
Physique et chimie pour le vivant et l’environnement › Physique et vivant / Physics and life
• Service des Photons Atomes et Molécules • Service des Photons Atomes et Molécules